微服务OJ在线判题
OJ常见概念:题目内存时间限制,题目描述,题目输入,题目输出,输入用例,测试用例
判题过程异步,提交之后,生成提交记录,有运行的结果
目的:用于在线评测编程题目代码的系统,能够根据用户提交代码,出题人预先设置的题目输入输出用例,编译代码,运行代码,判断代码运行结果是否正确
判题系统作为API开放,便于开发者制作自己的系统
功能:
题目模块:创建、删除、修改题目,搜索用户,在线做题,提交代码模块
用户模块:登陆注册
判题模块:提交判题、错误处理、自主实现代码沙箱、开放接口
在线做题:在线提交
拓展思路:支持多种语言、Remote Judge、普通评测、特殊评测、交互评测、在线自测
统计分析用户记录、权限校验、子任务分组评测、文件IO
层级划分
用户层:PC端网页
接入层:Nginx、API网关、负载均衡
业务层:项目模块、判题模块、用户模块
服务层:判题服务(代码沙箱) 用户鉴权服务、配置服务、通知服务
存储层:MySQL、Redis、RabbitMQ
资源层:Linux、Docker、K8S
后端模板
aop:用于全局权限校验,全局日志记录
common:万用的类,比如通用响应
config:用于接收application.yaml中的参数,初始化一些客户端的配置
constant:定义常量
job:任务相关、定时任务、单次任务
manager:服务层,包括 判题服务(代码沙箱) 用户鉴权服务、配置服务、通知服务
数据库表
题目表
题目标题
内容
标签
答案
提交数
通过数
judgeConfig :存储判题配置
judgeCase :judgeCase判题用例
CREATE TABLE `my_db`.`question` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键ID',
`title` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '问题标题',
`content` text NOT NULL COMMENT '问题内容',
`tags` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '标签列表,JSON格式',
`answer` text DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '参考答案',
`submit_count` int DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '提交次数',
`accepted_count` int DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '通过次数',
`judge_case` text DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '判题用例(JSON数组)',
`judge_config` text DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '判题配置(JSON对象)',
`user_id` int NOT NULL COMMENT '创建用户ID',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
`is_delete` tinyint DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '逻辑删除标记(0-未删除,1-已删除)',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_user_id` (`user_id`),
KEY `idx_create_time` (`create_time`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci COMMENT='问题表';
题目提交表
提交用户id
题目id
提交语言
用户提交代码
判题状态:判题中、带判题、成功、失败
判题信息:判题过程中得到的一些信息,例如程序失败的原因、程序执行消耗的空间、时间
判题信息枚举值:Accept 成功、Wrong Answer 答案错误、Compile Error编译错误、Memory Limit 空间不足、Time Out 超时、Waitting 等待中、Runtime Error 运行错误、System Error 系统错误
CREATE TABLE `my_db`.`submission` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '提交ID',
`question_id` bigint NOT NULL COMMENT '关联的题目ID',
`user_id` bigint NOT NULL COMMENT '提交用户ID',
`language` varchar(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '编程语言(java/python/cpp...)',
`code` text NOT NULL COMMENT '提交的代码',
`status` varchar(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'waiting' COMMENT '判题状态(waiting/running/success/failed)',
`judge_info` json DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '判题信息(JSON格式)',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '提交时间',
`update_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
`is_delete` tinyint NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '逻辑删除(0-正常,1-删除)',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_question_id` (`question_id`),
KEY `idx_user_id` (`user_id`),
KEY `idx_create_time` (`create_time`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci COMMENT='用户题目提交记录表';后端开发流程
1.根据功能设计表
2.自动生成对数据库的基本增删改查
3.编写Controller层,实现基本的增删改查和权限校验
4.去根据业务定制开发新的功能/编写新的代码
为了方便的处理json字段的某个对象,需要给对应的json字段配置独立的类
之所以这样是因为要方便前端进行数据的格式化,而不是整一个json字符串
分类VO DTO TO
基础的增删改查略
判题机
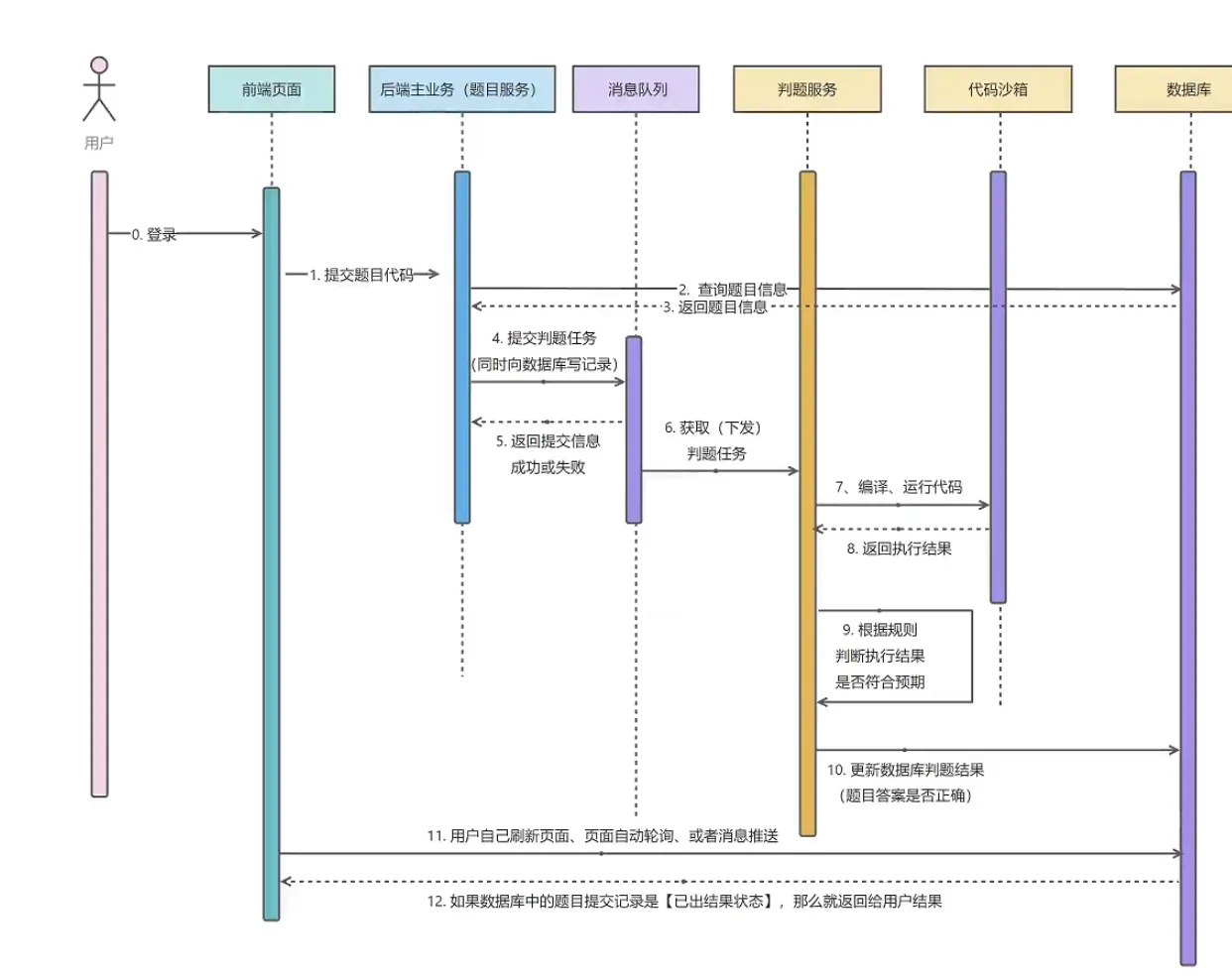
判题模块
调用代码沙箱,把代码和输入交给沙箱处理
代码沙箱:只负责接受代码和输入,返回编译运行的结果,不负责判题(可以作为独立的项目/服务,提供给其他的代码使用)
代码沙箱接受一组运行用例
如果是每个用例单独调用一次代码沙箱,会调用多次接口,需要多次网络传输、程序多次编译,记录程序状态
代码沙箱
定义代码沙箱接口,提高通用性
之后我们的项目只调用接口,不调用具体的实现类
/**
* 执行代码,获取编译运行结果
*/
public interface CodeSandBox {
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCode(ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest);
}分为了实例实现、第三方沙箱、自主实现沙箱
@Test
void contextLoads() {
String code = "int main() { }";
String language = "Java";
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("1 2", "3 4");
CodeSandBox sandbox = new ExampleCodeSandBox();
ExecuteCodeRequest request = ExecuteCodeRequest.builder().
code(code).
language(language).
inputList(inputList).
build();
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = sandbox.executeCode(request);
System.out.println(executeCodeResponse);
}还可以通过工厂模式进行对于new的替换,可以灵活调用传入参数进行使用不同的沙箱实现
public class CodeSandBoxFactory {
public CodeSandBox newInstance (String codeSandBoxName) {
switch (codeSandBoxName) {
case "example":
return new ExampleCodeSandBox();
case "remote":
return new RemoteCodeSandBox();
case "third":
return new ThirdPartyCodeSandBox();
default:
return null;
}
}
}@Test
void contextLoads() {
String code = "int main() { }";
String language = "Java";
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("1 2", "3 4");
CodeSandBox sandbox = new CodeSandBoxFactory().newInstance("example");
ExecuteCodeRequest request = ExecuteCodeRequest.builder().
code(code).
language(language).
inputList(inputList).
build();
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = sandbox.executeCode(request);
System.out.println(executeCodeResponse);
}参数配置化,将一些可选项交给用户自定义在配置文件中修改
配置在application中,通过Value注解取出类型
沙箱日志管理
通过静态代理实现,增添能力
@Slf4j
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CodeSandBoxProxy implements CodeSandBox {
private CodeSandBox codeSandBox;
@Override
public ExecuteCodeResponse executeCode(ExecuteCodeRequest executeCodeRequest) {
log.info("代码沙箱日志记录:----");
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = codeSandBox.executeCode(executeCodeRequest);
log.info("代码返回结果记录:----");
return executeCodeResponse;
}
}用代理类进行调用
public static void main(String[] args) {
String code = "int main() { }";
String language = "Java";
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("1 2", "3 4");
CodeSandBox sandbox = new CodeSandBoxFactory().newInstance("example");
ExecuteCodeRequest request = ExecuteCodeRequest.builder().
code(code).
language(language).
inputList(inputList).
build();
CodeSandBoxProxy proxy = new CodeSandBoxProxy(sandbox);
ExecuteCodeResponse executeCodeResponse = proxy.executeCode(request);
System.out.println(executeCodeResponse);
}判题服务
1.获取题目提交Id,获取到对应的题目,提交信息
2.更改题目状态,改为已提交
3.异步使用判断逻辑,调用沙箱,获取执行结果,之后根据沙箱的执行结果,设置题目的判题状态和信息
4.异步操作的时候,直接返回题目Id
判断逻辑
1.判断沙箱执行结果输出数量是否和预期输出数量相等(outlist.size() == inputlist.size())
2.依次每一项输出和预期输出是否相等
3.判题题目的限制是否符合要求
4.如果有异常情况进行额外处理
思考:如果我的盘体策略可能会有很多种,比如:我们的代码沙箱本身执行程序需要消耗时间,这个时间可能不同的编程语言是不同的,例如沙箱执行Java代码需要额外花10s,可以通过策略模式进行优化
我们对于不同的语言有不同的可定制化的判题策略,定义JudgeManager通过接口进行策略的使用,而策略的选择放在JudgeManager中传入language进行if-else的策略实现类的建立
代码沙箱
只负责接受代码和输入,返回编译运行的结果,不负责判题
原生实现
不借助第三方库,用最干净的方式实现代码沙箱
代码沙箱需要:接受代码->编译代码javac->执行代码java
一段代码示例,将其放在resource目录下
统一类名,对于用户代码有要求,限制类名为Main,且不用从用户代码中提取类名
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
System.out.println("结果是:" + (a + b));
}
}通过javac进行编译,java运行来执行
javac -encoding UTF-8 Main.java
java Main 4 6打印出结果
结果是:10核心流程
核心实现思路:用程序代替人工,用程序执行命令,编译执行代码
Java进程执行管理类:Process
1.保存用户代码为文件
2.编译代码得到class文件
3.执行代码,得到输出结果
4.收集整理输出结果
5.文件清理
6.错误处理,提升程序健壮性
新建目录:将用户代码放到一个独立的文件夹中
完成一个执行进程的工具类
package com.sandbox.utils;
import com.sandbox.model.ExecuteMessage;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
* 进程工具类
*/
public class ProcessUtils {
public static ExecuteMessage runProcess(String command) throws InterruptedException, IOException {
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder error = new StringBuilder();
int exitCode = process.waitFor();
if (exitCode == 0) {
System.out.println("Success...");
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
String compileMessage;
while((compileMessage = reader.readLine()) != null) {
message.append(compileMessage);
}
System.out.println(message);
} else {
System.out.println("Fail!! " + "exitCode:" + exitCode);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getErrorStream()));
String compileMessage;
while((compileMessage = reader.readLine()) != null) {
error.append(compileMessage);
}
System.out.println(error);
}
ExecuteMessage executeMessage = new ExecuteMessage();
executeMessage.setExitCode(exitCode);
executeMessage.setMessage(message.toString());
executeMessage.setErrorMessage(error.toString());
return executeMessage;
}
}package com.sandbox.service;
import cn.hutool.core.io.FileUtil;
import com.sandbox.model.ExecuteCodeRequest;
import com.sandbox.model.ExecuteCodeResponse;
import com.sandbox.model.ExecuteMessage;
import com.sandbox.utils.ProcessUtils;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class JavaNativeCodeSandBox implements CodeSandBox {
private static final String GLOBAL_CODE_DIR_NAME = "tmpCode";
private static final String GLOBAL_JAVA_CLASS_NAME = "Main.java";
@Override
public ExecuteCodeResponse execute(ExecuteCodeRequest request) {
List<String> inputList = request.getInputList();
String code = request.getCode();
String language = request.getLanguage();
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String globalCodePath = userDir + File.separator + GLOBAL_CODE_DIR_NAME;
System.out.println(globalCodePath);
if (!FileUtil.exist(globalCodePath)) {
FileUtil.mkdir(globalCodePath);
}
//把用户的代码分级隔离存放
String userCodeParentPath = globalCodePath + File.separator + UUID.randomUUID();
String userCodePath = userCodeParentPath + File.separator + GLOBAL_JAVA_CLASS_NAME;
System.out.println(userCodePath);
File userCodeFile = FileUtil.writeString(code, userCodePath, "UTF-8");
String compileCmd = String.format("javac -encoding UTF-8 %s", userCodeFile.getAbsoluteFile());
ExecuteMessage executeCompileMessage;
try {
executeCompileMessage = ProcessUtils.runProcess(compileCmd);
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//运行指令执行
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for(String input: inputList) {
String runCmd = String.format("java -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -cp %s Main %s", userCodeParentPath, input);
try {
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(runCmd);
int exitCode = process.waitFor();
if (exitCode == 0) {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
result.add(line);
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException | IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// for(String ans : result) {
// System.out.println(ans);
// }
ExecuteCodeResponse response = new ExecuteCodeResponse();
// response.setMessage("编译信息:" + executeCompileMessage.toString() + "\n运行信息: " +runExecuteMessage.toString());
response.setOutputList(result);
return response;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JavaNativeCodeSandBox sandBox = new JavaNativeCodeSandBox();
ExecuteCodeResponse response = sandBox.execute(ExecuteCodeRequest.builder().
language("java").
code("public class Main {\n" +
" public static void main(String[] args) {\n" +
" int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);\n" +
" int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);\n" +
" System.out.println(\"结果是:\" + (a + b));\n" +
" }\n" +
"}").
inputList(Arrays.asList("1 3", "5 7")).
build());
System.out.println(response);
}
}在结束后将生成的字节码文件和写入源文件删除
if(userCodeFile.getParentFile() != null) {
boolean del = FileUtil.del(userCodeParentPath);
System.out.println("删除" + (del ? "成功" : "失败"));
}安全风险
用户提交恶意代码
1.时间:提交无限睡眠代码,例如sleep
2.空间:占用空间不释放,例如递归
JVisualVM可以连接到JVM虚拟机监控虚拟机
3.通过读取文件得到配置文件获取其中的配置信息
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String userDirectory = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String filePath = userDirectory + "/src/main/resources/application.yaml";
List<String> allLines = Files.readAllLines(Paths.get(filePath));
for (String line : allLines) {
System.out.println(line);
}
}
}返回的结果中存在结果,加入敏感信息放在这里面就会有泄露风险
ExecuteCodeResponse(outputList=[spring:, application:, name: sandbox, server:, port: 8080, spring:, application:, name: sandbox, server:, port: 8080], message=null, status=0, judgeInfo=null)4.将恶意程序写入服务器目录
之后将写入的程序通过服务器环境进行执行,这样就非常的危险了
5.执行高位命令
例如rm -rf /* 等
解决方式
1.超时控制 2.限制给用户的资源 3.禁用用户的读写权限(黑白名单/文件、网络、执行) 4.对于整个环境进行隔离
超时控制:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(20000);
System.out.println("睡眠完毕");
}
}Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(runCmd);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
process.destroy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}).start();资源分配:
在启动Java的时候可以指定JVM参数 :-Xmx256m
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<byte[]>();
while(true) {
list.add(new byte[0]);
}
}
}String runCmd = String.format("java -Xmx256M -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -cp %s Main %s", userCodeParentPath, input);操作限制
运用字典树,对于代码中的读写,执行等关键词进行限制
Java安全管理器是Java提供保护JVM,java程序的
Docker代码沙箱
Docker基本用法,命令行,Java客户端
Docker实现代码沙箱
提升Docker沙箱的安全性
实现原理:
1.Docker运行在Linux内核上
2.CGroups:实现了容器的资源隔离,底层是Linux CGroup,能够控制进程使用的资源
3.Network网络:实现容器的网络隔离,docker容器内部的网络互不影响
4.Namespaces命名空间:可以把进程隔离在不同的命名空间下,每个容器都有自己的命名空间,不同的命名空间下的进程互不影响
5.Storage存储空间:容器内的文件相互隔离
DockerClientConfig:用于定义初始化DockerClient配置
DockerHttpClient:用于向Docker守护进程(操作Docker的接口)低层封装
DockerClient:真正和Docker守护进程交互的SDK,是高层封装,对于DockerHttpClient的再次封装

