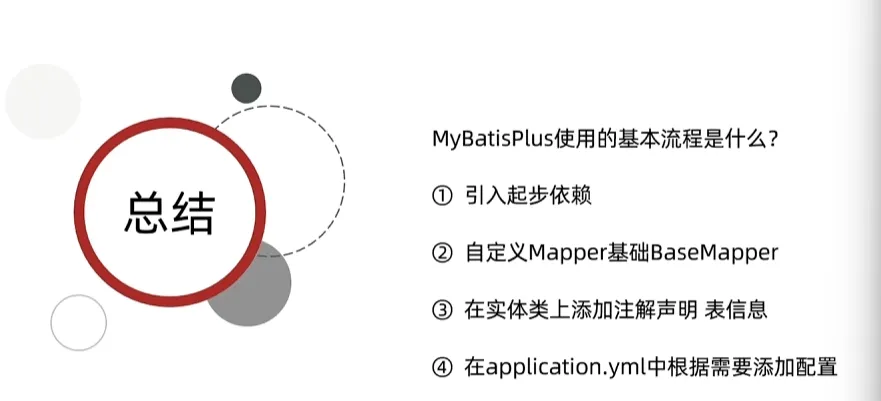
MyBatis-plus笔记
MyBatisPlus是MyBatis的增强版,旨在简化单表SQL的编写
基本使用
spring:
application:
name: **
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://thrinisty.fun:3306/thrina
username: root
password: **相关依赖:这个依赖可以直接替代原先的MyBatis依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-spring-boot3-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.33</version>
</dependency>User用TableName注解指定表格
@Data
@TableName("tb_user")
public class User {
private int id;
private String phone;
private String password;
private String nickName;
private String icon;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}对于Mapper我们通过继承BaseMapper
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
@Select("SELECT id, phone, password, nick_name AS nickName, icon, create_time AS createTime," +
" update_time AS updateTime FROM tb_user WHERE id = #{id}")
User getUserById(int id);
}@Test
void contextLoads() {
User user = userMapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}
@Test
void testMybatisPlus() {
User user = userMapper.selectById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}常用注解
MyBatisPlus是通过扫描实体类,并基于反射获取实体类信息作为数据库表信息
类名驼峰转下划线作为表名
名为id的字段作为主键
变量名驼峰转下划线作为表的字段名称但是如果不符合以上的配置我们就需要手动使用注解进行配置
@TableName:指定表名,我们还可以
@TableId:指定表的主键字段信息,我们还可以使用type指定主键id的生成策略
@TableField:指定表的普通字段信息
如下是一个完整的配置entity对象,有一些字段或者id是可以省略的,因为符合约定的配置
@Data
@TableName("tb_user")
public class User {
@TableId("id")
private int id;
@TableField("phone")
private String phone;
@TableField("password")
private String password;
@TableField("nick_name")
private String nickName;
@TableField("icon")
private String icon;
@TableField("create_time")
private LocalDateTime createTime;
@TableField("update_time")
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}加入我们的字段属于SQL中的关键字,我们可以使用TableField来加上“字符包裹
我们如果一个对象中有不是数据库的字段我们可以通过设置exist=false来进行设置
@Data
@TableName("tb_user")
public class User {
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO)
private int id;
@TableField("phone")
private String phone;
@TableField("password")
private String password;
@TableField("nick_name")
private String nickName;
@TableField("icon")
private String icon;
@TableField("create_time")
private LocalDateTime createTime;
@TableField("update_time")
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
@TableField(exist = false)
private LocalDateTime LogicTime;
}常见配置
这配置中可以进行一些参数的设置

核心功能
条件构造器
MyBatisPlus支持各种各样的复杂where条件,可以满足日常开发的所有需求
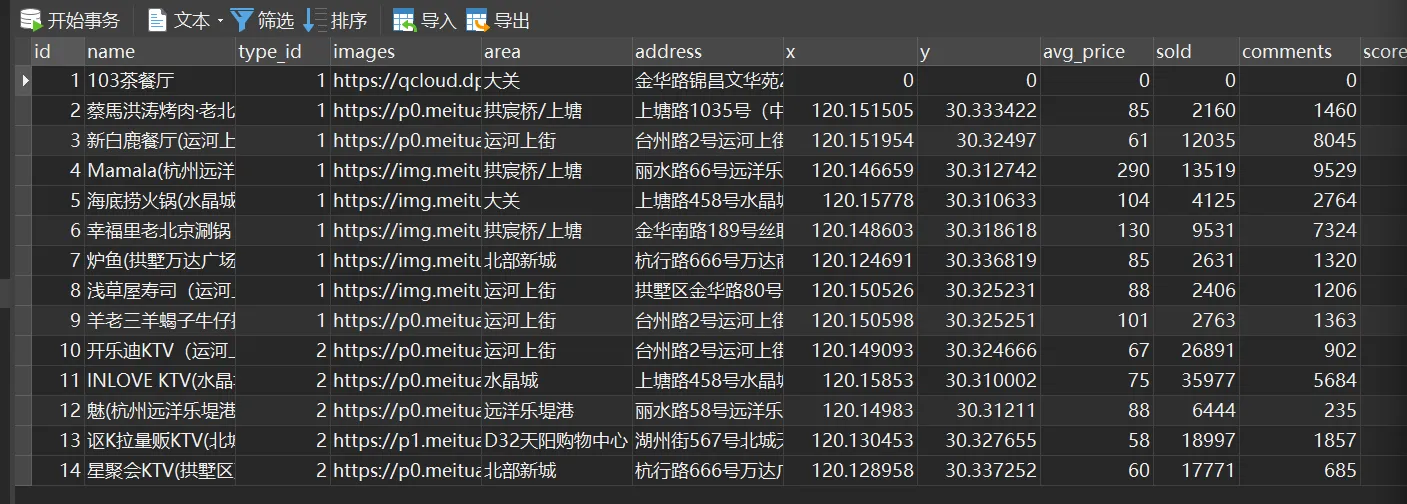
我们有这样一个结构
@Data
@TableName("tb_shop")
public class Shop {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
int id;
String name;
int typeId;
String images;
String area;
String address;
double x;
double y;
int avgPrice;
int sold;
int comments;
int score;
String openHours;
LocalDateTime createTime;
LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
现在我们需要用MyBatis完成如下功能
1.查询avg_price大于50且得分小于40的商店的id,name,area字段
如果是SQL写为如下,用QueryWrapper实现
select id, name, area from tb_shop where score < 40 and avg_price > 50@Test
void testMybatisPlus() {
QueryWrapper<Shop> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.select("id", "name", "area")
.lt("score", 40)
.gt("avg_price", 50);
List<Shop> shops = shopMapper.selectList(wrapper);
for(Shop shop : shops) {
System.out.println(shop);
}
}Shop(id=10, name=开乐迪KTV(运河上街店), typeId=0, images=null, area=运河上街, address=null, x=0.0, y=0.0, avgPrice=0, sold=0, comments=0, score=0, openHours=null, createTime=null, updateTime=null)在实际开发中我们其实更加推荐于使用Lambda的形式获取属性名称而非硬编码的方式
@Test
void testMybatisPlus() {
LambdaQueryWrapper<Shop> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<Shop>().lambda();
wrapper.select(Shop::getId, Shop::getName, Shop::getArea)
.lt(Shop::getScore, 40)
.gt(Shop::getAvgPrice, 50);
List<Shop> shops = shopMapper.selectList(wrapper);
for(Shop shop : shops) {
System.out.println(shop);
}
}2.更新103茶餐厅的x为101.02,y为120.01
update tb_shop set x = 101.02, y = 120.01 where name = "103茶餐厅"@Test
void contextLoads() {
Shop shop = new Shop();
shop.setX(101.02);
shop.setY(120.01);
QueryWrapper<Shop> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("name", "103茶餐厅");
int update = shopMapper.update(shop, wrapper);
System.out.println(update);
}3.更新1、2、4商店,使其score得分加10
update tb_shop set score = score + 10 where id in (1,2,4)我们给予UpdateWrapper实现
@Test
void contextLoads() {
UpdateWrapper<Shop> wrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
wrapper.setSql("score = score + 10").in("id", List.of(1, 2, 4));
shopMapper.update(null, wrapper);
}自定义SQL
可以利用MyBatisPlus的Wrapper来构建复杂的where条件,然后自定义SQL语句中的剩下一个部分
我们在上述的时候用的UpdateWrapper是在业务层进行代码的编写的,但是在实际开发的过程中我们往往规定SQL只能在Mapper中提供方法供以Service层调用,这个时候我们就需要使用到自定义SQL
需求:将id指定范围内的用户余额扣除指定值,在业务层指定查询条件,SQL语句构造在xml文件中
@Test
void contextLoads() {
List<Integer> idList = List.of(1, 2, 4);
LambdaUpdateWrapper<Shop> wrapper = new UpdateWrapper<Shop>().lambda();
wrapper.in(Shop::getId, idList);
int amount = 5;
shopMapper.updateScoreByIds(wrapper, amount);
}写上对应的接口mapper,注意这里一定要ew标注wrapper
@Mapper
public interface ShopMapper extends BaseMapper<Shop> {
void updateScoreByIds(@Param("ew") LambdaUpdateWrapper<Shop> wrapper, @Param("amount") int amount);
}在Mapper中进行拼接
<update id="updateScoreByIds">
update tb_shop set score = score + #{amount} where ${ew.sqlSegment}
</update>Service接口
Service业务层使用Mapper层级的接口进行业务的编写,MyBatisPlus帮助我们实现了很对Service的方法,我们使用对应服务的接口继承IService接口即可使用相关的方法,我们的实现类继承于业务接口但是因为没有实现IService接口的相关方法我们还需要用业务的实现类去继承ServiceImpl的实现方法
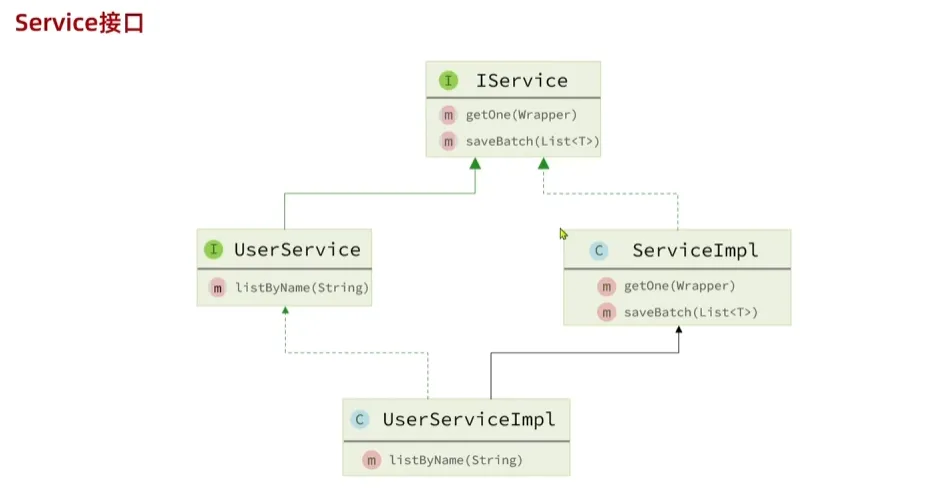
public interface ShopService extends IService<Shop> {
}@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ShopMapper, Shop> implements ShopService {
}此时我们注入ShopService就可以使用其下的方法,其方法基于ShopMapper实现
@Test
void testShopService() {
Shop shop = shopService.getById(1);
System.out.println(shop);
}网络请求示例
@Service
public class ShopServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ShopMapper, Shop> implements ShopService {
@Autowired
private ShopMapper shopMapper;
@Override
public void updateScore(int id, int amount) {
//实现以下updateScore方法
LambdaUpdateWrapper<Shop> wrapper= new UpdateWrapper<Shop>().lambda();
wrapper.eq(Shop::getId, id);
shopMapper.updateScoreByIds(wrapper, amount);
}
}@RestController
@RequestMapping("shop")
public class ShopController {
@Autowired
private ShopService shopService;
@PostMapping
public void addShop(@RequestBody Shop shop) {
shopService.save(shop);
}
@DeleteMapping("{id}")
public void deleteShop(@PathVariable int id) {
shopService.removeById(id);
}
@GetMapping("{id}")
public Shop getShop(@PathVariable int id) {
return shopService.getById(id);
}
@GetMapping
public List<Shop> getShops(@RequestParam("id") List<Integer> list) {
QueryWrapper<Shop> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.in("id", list);
return shopService.list(wrapper);
}
@PutMapping("/score/{id}/{amount}")
public void updateScore(@PathVariable int id, @PathVariable int amount) {
shopService.updateScore(id, amount);
}
}Lambda查询
我们在之前多条件查询使用的是动态SQL来进行条件的选择性过滤,现在基于Lambda查询我们也可以做到相同的功能
常规方式:通过动态SQL进行查询
@Override
public List<Shop> multiQuery(ShopQueryEntity query) {
return shopMapper.multiSelect(query);
}<select id="multiSelect" resultType="com.nwpu.mybatistest.entity.Shop">
SELECT id, name, type_id, images, area, address, x, y, avg_price,
sold, comments, score, open_hours, create_time, update_time
FROM tb_shop
<where>
<if test="id != null">
AND id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="name != null">
AND name like #{id}
</if>
<if test="typeId != null">
AND type_id = #{typeId}
</if>
</where>
</select>而我们Lambda查询实现如下:在业务层使用lambdaQuery传入条件,最后的结果以list返回,同样的我们也可以count计算数量,one返回一个,page分页返回,方法非常多样
@Override
public List<Shop> multiQueryByLambda(ShopQueryEntity query) {
List<Shop> list = lambdaQuery().eq(query.getId() != null, Shop::getId, query.getId())
.like(query.getName() != null, Shop::getName, query.getName())
.eq(query.getTypeId() != null, Shop::getTypeId, query.getTypeId())
.list();
return list;
}同样的我们也可以进行一些其他逻辑的编写:当amount小于100的时候才会用amount更新指定id的score,记得最后update
@Override
public void updateScoreByLambda(int id, int amount) {
lambdaUpdate()
.set(amount < 100, Shop::getScore, amount)
.eq(Shop::getId, id)
.update();
}批量新增
通过saveBatch,传入list集合,可以一次性传入多条数据,性能部分提升
List<Shop> shops = List.of(shop);
shopService.saveBatch(shops);但是我们批处理性能最好的应该是如下的方式,这会将value写在一条SQL中
url: jdbc:mysql://thrinisty.top:3306/redis?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=UTF-8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true代码不需要改变,加上rewriteBatchedStatements=true配置即可,加上这一条配置数据库驱动就会把一条条SQL合并为一条SQL执行
拓展功能
静态工具
在使用上和分层的注入对象大体类似,只是不需要去注入,只需要Db的静态方法传入对象字节码对象即可使用,用这个静态工具我们可以放置一些业务层之间的注入依赖,但是在实际尽量还是使用分层,更加符合规范
public void addUserPoints(List<Long> userIds, int points) {
Db.lambdaUpdate(User.class)
.in(User::getId, userIds)
.setSql("points = points + " + points)
.update();
}逻辑删除
逻辑删除是基于代码的逻辑模拟删除的效果,不会真的删除数据,可以定义一个字段为1代表该数据被删除,当增改查的时候只对于字段标记为0的数据进行操作
我们后续如果误删数据也可以及时恢复,将对应逻辑删除字段设置成为0即可
@Data
public class User {
@TableId
private Long id;
private String name;
@TableLogic
private Integer deleted; // 1表示已删除,0表示未删除(类型可以是int/boolean/String等)
}
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
logic-delete-field: deleted # 全局逻辑删除字段名(与实体类字段名一致)
logic-not-delete-value: 0 # 未删除的值
logic-delete-value: 1 # 已删除的值配置完成后我们的方法逻辑就会改变,符合逻辑删除的方式
userMapper.deleteById(1L);
// SQL: UPDATE user SET deleted=1 WHERE id=1 AND deleted=0
List<User> list = userMapper.selectList(null);
// SQL: SELECT * FROM user WHERE deleted=0当然也会有危险:垃圾数据越来越多,SQL中全部都需要对逻辑字段做一个判断,影响查询效率。
ps:但是从我实习的公司看来,似乎逻辑删除还是很重要滴,在大的互联网厂或者网络安全公司,数据的价值往往被放的非常高
枚举处理器
解决枚举转换

Json处理器
1.给对应属性添加实体,添加注解,添加Json处理器
2.给表添加autoResultMap设置为True
@Data
@TableName(value = "product", autoResultMap = true)
public class Product {
private Long id;
// 方案1:使用 MyBatis-Plus 内置的 Jackson 处理器
@TableField(typeHandler = JacksonTypeHandler.class)
private Map<String, Object> attributes;
// 方案2:映射到具体 POJO
@TableField(typeHandler = JacksonTypeHandler.class)
private ProductDetail detail;
}
@Data
public class ProductDetail {
private String color;
private Integer weight;
}分页插件
用原先的PageHelper实现分页,我们引入依赖后发生冲突,我们需要手动的排除mybatis依赖(PageHelper 引入了旧版 MyBatis,与 MyBatis-Plus 的 MyBatis 版本冲突)
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
<exclusions>
<!-- 排除潜在的冲突依赖 -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>之后我们采用常规的方式即可完成分页查询
@Override
public PageInfo<Shop> multiQuery(ShopQueryEntity query, int pageNum, int pageSize) {
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pageSize);
List<Shop> shops = shopMapper.multiSelect(query);
PageInfo<Shop> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(shops);
return pageInfo;
}
