931 字
5 分钟
LeetCode刷题(组合总和,公共祖先)
组合总和
题目描述
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
输出:[[2,2,3],[7]]
解释:
2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。
7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。
仅有这两种组合。示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8
输出: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]示例 3:
输入: candidates = [2], target = 1
输出: []题解
经典的回溯法求解:思路类似于之前做过的全排列,终止判断条件为target=0或者数组遍历完成target 任然不满足条件
在调用的基础上,分为了跳过当前位置的数字,以及使用当前数字两种情况,在使用的时候使list增加被使用的数字,在递归调用传入新的目标数字和后删除
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
fun(candidates, target, 0);
return result;
}
public void fun(int[] candidates, int target, int idx) {
if(target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list));
return;
}
if(idx == candidates.length) {
return;
}
fun(candidates, target, idx + 1);
int newNum = candidates[idx];
int newTarget = target - newNum;
if(newTarget >= 0) {
list.add(newNum);
fun(candidates, newTarget, idx);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
}
}
}二叉树的最近公共祖先
题目描述
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例 1:
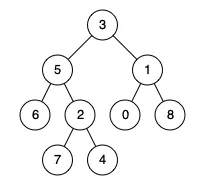
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出:3
解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。示例 2:

输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出:5
解释:节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5 。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
输出:1题解
如果当前节点是 null 或者是目标节点之一(p 或 q),直接返回当前节点。 递归左右子树: 左子树返回值为 l,右子树返回值为 r。 根据左右子树的返回值判断: 如果左子树返回 null,说明 p 和 q 都在右子树中,返回右子树的结果。 如果右子树返回 null,说明 p 和 q 都在左子树中,返回左子树的结果。 如果左右子树都不为 null,说明当前节点就是最近公共祖先,返回当前节点。
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode l = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode r = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
TreeNode father;
if(l == null) {
father = r;
} else {
if(r == null) {
father = l;
} else {
father = root;
}
}
return father;
}
}或者通过三目运算符简化一下
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return left == null ? right : (right == null ? left : root);
}
} LeetCode刷题(组合总和,公共祖先)
https://thrinisty.github.io/Blog/posts/leetcode刷题组合总和公共祖先/ 
