1175 字
6 分钟
LeetCode刷题(完全二叉树的节点个数、填充右侧节点、搜索树迭代器)
完全二叉树的节点个数
题目描述
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层(从第 0 层开始),则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 1:
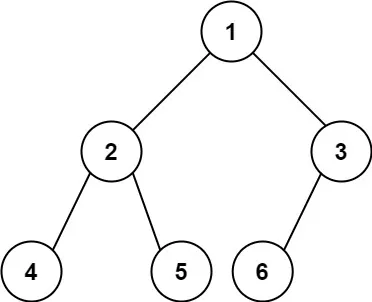
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:0示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5 * 104] 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 104- 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
**进阶:**遍历树来统计节点是一种时间复杂度为 O(n) 的简单解决方案。你可以设计一个更快的算法吗?
题解
解法一:通过递归求解,时间复杂度为O(n),没有用到二叉树的性质
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = countNodes(root.left);
int right = countNodes(root.right);
return left + right + 1;
}
}解法二:计算所有两侧的层高,如果相同则代表左树是满二叉树,节点个数为1 << left,还需要算右数的节点数
如果层高不同则代表右树是满二叉树,还需要计算左侧的满二叉树节点数量,将结果相加
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = countLevel(root.left);
int right = countLevel(root.right);
if(left == right) {
return (1 << left) + countNodes(root.right);
} else {
return countNodes(root.left) + (1 << right);
}
}
public int countLevel(TreeNode root) {
int level = 0;
while(root != null) {
level++;
root = root.left;
}
return level;
}
}填充右侧节点
题目描述
给定一个二叉树:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL 。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL 。
示例 1:
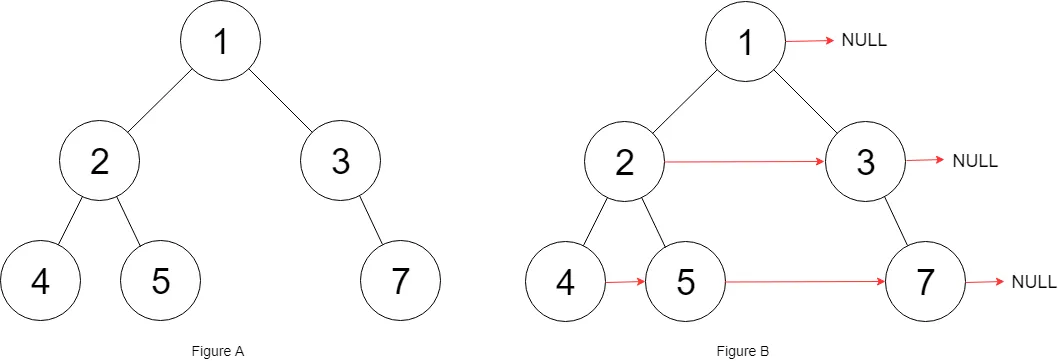
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。序列化输出按层序遍历顺序(由 next 指针连接),'#' 表示每层的末尾。示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]题解
运用层序遍历,将每一层的元素顺次链接即可
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if(root == null) return null;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int n = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Node node = queue.poll();
if(i < n - 1) {
node.next = queue.peek();
}
if(node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}二叉搜索树迭代器
题目描述
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器类BSTIterator ,表示一个按中序遍历二叉搜索树(BST)的迭代器:
BSTIterator(TreeNode root)初始化BSTIterator类的一个对象。BST 的根节点root会作为构造函数的一部分给出。指针应初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,且该数字小于 BST 中的任何元素。boolean hasNext()如果向指针右侧遍历存在数字,则返回true;否则返回false。int next()将指针向右移动,然后返回指针处的数字。
注意,指针初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,所以对 next() 的首次调用将返回 BST 中的最小元素。
你可以假设 next() 调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用 next() 时,BST 的中序遍历中至少存在一个下一个数字。
示例:
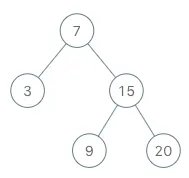
输入
["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"]
[[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]
输出
[null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false]
解释
BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]);
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 3
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 7
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 9
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 15
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 20
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 False题解
运用栈来进行状态存储
先回顾一下中序遍历的非递归方式
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode p = root;
while(!stack.isEmpty() || p != null) {
while(p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
p = stack.pop();
result.add(p.val);
p = p.right;
}
return result;
}
}更改为迭代器的方式
class BSTIterator {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode p;
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
p = root;
}
public int next() {
while(p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
TreeNode target = stack.pop();
p = target.right;
return target.val;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return !stack.isEmpty() || p != null;
}
} LeetCode刷题(完全二叉树的节点个数、填充右侧节点、搜索树迭代器)
https://thrinisty.github.io/Blog/posts/leetcode刷题完全二叉树的节点个数填充右侧节点搜索树迭代器/ 
