听课笔记
Java中的重载
Java中允许同名方法的存在,这种情况下要求同名方法的参数不同
以下是一个具体的案例
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
myTool.Print(1);
myTool.Print('1');
myTool.Print("This is overload");
}
}
class Tool {
public void Print(int n) {
System.out.println(n);
}
public void Print(char n) {
System.out.println(n);
}
public void Print(String n) {
System.out.println(n);
}
}重载除了形式参数类型不一样还可以数量不一样
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
System.out.println(myTool.Test(1, 2));
System.out.println(myTool.Test(1, 2.0));
System.out.println(myTool.Test(1.0, 2));
System.out.println(myTool.Test(1, 2, 3));
}
}
class Tool {
public int Test(int m, int n) {
return m + n;
}
public double Test(int m, double n) {
return m + n;
}
public double Test(double m, int n) {
return m + n;
}
public int Test(int n1, int n2, int n3) {
return n1 + n2 + n3;
}
}练习题目
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
System.out.println(myTool.Test(1, 2));
System.out.println(myTool.Test(1.0, 2.0));
System.out.println(myTool.Test(1.0, 3.0, 2.0));
}
}
class Tool {
public int Test(int m, int n) {
return m > n ? m : n;
}
public double Test(double m, double n) {
return m > n ? m : n;
}
public double Test(double m, double n, double i) {
double max = m > n ? m : n;
return max > i ? max : i;
}
}Java中的可变参数
java中允许将同一个类中多个同名同功能但参数个数不同的方法,封装为一个方法,可以通过可变参数实现
基本语法
访问修饰符 返回类型 方法名称(数据类型… 形参名称)
使用可变参数的时候作为数组来进行使用
以下是一个可变参数的代码示例,可以计算 n 个数据的和
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
System.out.println(myTool.Test());
System.out.println(myTool.Test(1.0, 2.0));
System.out.println(myTool.Test(1.0, 3.0, 2.0));
}
}
class Tool {
public double Test(double... nums) {
System.out.println("接收了" + nums.length + "个参数");
double result = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
result +=nums[i];
}
return result;
}
}可变参数的使用细节
1.可变参数的参数个数可以是 0 个或者任意多个
2.可变参数的实参可以为数组(但是不允许可变的传统数组)
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3};
myTool.Test(arr);
}
}
class Tool {
public void Test(int... nums) {
System.out.println("接收了" + nums.length + "个参数");
}
}//如下的代码编译错误
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
int arr1[] = {1, 2, 3};
int arr2[] = {1, 2, 3};
int arr3[] = {1, 2, 3};
myTool.Test(arr1);
myTool.Test(arr1, arr2, arr3);
}
}
class Tool {
public void Test(int... nums[]) {
System.out.println("接收了" + nums.length + "个参数");
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
System.out.println("第"+ i + "个数组");
for(int j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(nums[i][j] + " ");
}
}
}
}
3.可变参数的本质就是数组
4.可变参数可以和普通类型的参数一起放在形参列表,但是必须要保证可变参数在最后
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3};
myTool.Test("arr", arr);
// myTool.Test(arr, "arr");
}
}
class Tool {
public void Test(String str, int... nums) {
// public void Test(int... nums, String str) {
System.out.println("字符串" + str);
System.out.println("接收了" + nums.length + "个参数");
}
}5.一个形参列表只能出现一个可变参数 ,不允许多个可变参数
以下是一个练习题目 其目的是接收学生的名字和不确定个数的成绩
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
double result = myTool.Test("Li Wen", 100.0, 33.0, 220.0);
System.out.println("学生的总成绩是" + result);
}
}
class Tool {
public double Test(String str, double... nums) {
System.out.println("学生" + str);
System.out.println("有" + nums.length + "个成绩");
double result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
result += nums[i];
}
return result;
}
}Java中的作用域
局部变量一般是在成员方法中定义的变量
全局变量(属性)
也就是属性,作用于是整个类体,方法可以使用他们
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
}
}
class Tool {
String name = "jack";
public void Test() {
int n = 10;
System.out.println(name);
}
public void Test1() {
//System.out.println(n);
}
}局部变量
除了属性外的其他变量,作用域在代码块中
注意要点
全局变量可以不赋值,有默认值,局部变脸必须要赋值才可以使用,因为没有默认值
作用域注意事项
1.属性和局部变量可以重名,访问时遵循就近原则
2.在同一个作用域内,同一个成员方法中,两个局部变量不能够重名
这里 java 和 c 语言中存在不同
- C语言:允许在嵌套的代码块中重新定义与外层同名的变量,内层的变量会遮蔽外层的变量。
- Java:不允许在嵌套的代码块中重新定义与外层同名的变量,编译器会报错。
3.属性的生命周期长于局部变量,属性随着对象创建而创建,随对象的销毁而销毁,局部变量是在方法调用时产生,调用完成后销毁
4.全局变量可以被本类使用和其他的类使用(通过对象调用完成)局部变量只可以在本类的对应方法中使用
也可以支持对象之间的相互传对象本身,编译通过,但是在实际编写代码的时候应该尽量避免相互依赖
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
Person human = new Person();
myTool.Test(human);
human.Test(myTool);
}
}
class Person {
String name = "jack";
public void Test(Tool human) {
System.out.println(human.name);
}
}
class Tool {
String name = "liry";
public void Test(Person human) {
System.out.println(human.name);
}
}5.全局变量可以被访问修饰符使用,而局部变脸不行
Java中的构造器
构造方法,其中它的方法名字和类的名字相同
构造方法没有返回值,也不能使用返回类型
[修饰符] 方法名 (形参列表) {
方法体;
}一个简单的入门代码示例
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool("thrinisty", 14);
myTool.test();
}
}
class Tool {
String name;
int age;
public Tool(String n, int m) {
name = n;
age = m;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("名字是" + name + "年龄是" + age);
}
}
构造器的使用细节
1.构造器可以被重载,可以定义多个构造器
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool("thrinisty");
//在这里没有指定年龄,使用的是第二个构造方法
myTool.test();
}
}
class Tool {
String name;
int age;
public Tool(String n, int m) {
name = n;
age = m;
}
public Tool(String n) {
name = n;
age = 0;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("名字是" + name + "年龄是" + age);
}
}2.构造器的名称要和类的名称相同
3.构造器没有返回值
4.构造器不会创建兑现,他的目的只是为了完成初始化
5.在创建对象的时候会自动调用构造方法,不允许主动调用构造方法
6.如果没有定义构造方法,系统会自动给类生成一个无参数的构造器
可以使用 javap 反编译工具进行验证
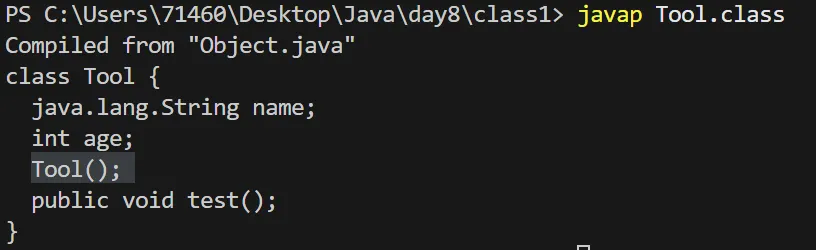
7.一旦定义了构造方法,默认的无参构造器就被覆盖了,如果需要使用要显示定义一次
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
myTool.test();
}
}
class Tool {
String name;
int age;
public Tool(){}
public Tool(String n) {
name = n;
age = 0;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("名字是" + name + "年龄是" + age);
}
}Java中的this关键字
java虚拟机会给每一个对象分配一个this,这个this可以被当成为一个属性,这个属性是一个引用指向对象自己
以下是一个代码示例,this 指的就是Person这个类,可以通过this 来引用类的属性
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person human = new Person("lory", 18);
human.test();
}
}
class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("名字是" + name + "年龄是" + age);
}
}this在内存中的存在形式
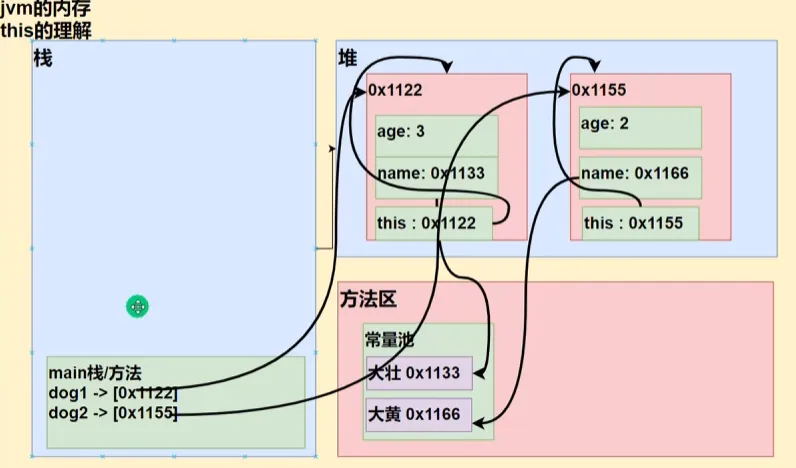
我们也可以通过哈希编码来验证这个this指向的内容和对象引用的内存地址是一样的
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person human = new Person("lory", 18);
System.out.println("对象的哈希值是" + human.hashCode());
human.test();
}
}
class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("this引用的哈希值是" + this.hashCode());
}
}运行结果
PS C:\Users\71460\Desktop\Java\day8\class1> java Object
对象的哈希值是1311053135
this引用的哈希值是1311053135this关键字的使用细节
1.this 可以用来访问本类的属性,方法,构造器
2.this用于区分当前类的属性和局部变量
3.this不能够被类定义的外部使用,只可以在类定义的方法中使用
4.访问构造器语法this (参数列表),只可以在构造器中使用(还必须将this语句放在第一条语句)
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person human = new Person();
human.test();
}
}
class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person() {
this("jack", 100);//第一条语句
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("对象 " + this.name + this.age);
}
}this关键字用于引用当前对象的实例。在Person类中,this.name和this.age明确地指向当前对象的name和age属性。然而,在test方法中,直接使用name和age也可以访问这些属性,因为它们在当前对象的上下文中是可见的
在代码规范上:开发团队或代码风格指南可能要求使用this来访问实例变量,以增加代码的可读性和一致性。
this练习题目
判断类属性是否相同
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person human1 = new Person();
Person human2 = new Person("lory", 11);
if(human1.compareTo(human2)) {
System.out.println("对象属性相同");
} else {
System.out.println("对象属性不同");
}
}
}
class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person() {
this("jack", 100);
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public boolean compareTo(Person another) {
return another.name.equals(this.name) && another.age == this.age;
}
}章节作业
1.找到double数组中最大值返回这个最大值
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double arr[] = {1.3, 2.5, 1.1, 3.2, 5.2};
Tool myTool = new Tool();
System.out.println("最大值是" + myTool.findMax(arr));
}
}
class Tool{
public double findMax(double[] arr) {
double max = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(max < arr[i]) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}2.找到字符串元素的下标
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String arr[] = {"1.3", "2.5", "1.1", "3.2", "5.2"};
Tool myTool = new Tool();
System.out.println("元素下标是" + myTool.findString(arr, "1.1"));
}
}
class Tool{
public int findString(String[] arr, String target) {
int index = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(target.equals(arr[i])){
index = i;
return index;
}
}
return index;
}
}3.改变书本价格
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book myBook = new Book("爱丽丝", 133.0);
myBook.updatePrice();
System.out.println(myBook.price);
}
}
class Book{
String name;
double price;
public Book(String name, double price){
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public void updatePrice() {
if(this.price > 150) {
this.price = 150;
} else if(this.price <= 150 && this.price > 100) {
this.price = 100;
} else {}
}
}4.实现数组的复制功能,元素和旧数组一样
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool();
int oldArr[] = {1, 3, 5, 6};
myTool.print(oldArr);
int newArr[] = myTool.copyArr(oldArr);
myTool.print(newArr);
}
}
class Tool{
public int[] copyArr(int[] arr) {
int newArr[] = new int[arr.length];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
newArr[i] = arr[i];
}
return newArr;
}
public void print(int[] arr) {
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}5.定义一个圆类,属性有半径, 提供周长方法,提供面积方法
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool(1.9);
System.out.println("面积是" + myTool.area());
System.out.println("周长是" + myTool.lan());
}
}
class Tool{
double r;
public Tool(double r) {
this.r = r;
}
public double area() {
return Math.PI * r * r;
}
public double lan() {
return Math.PI * r * 2;
}
}6.一个简单的除法计算器
其中返回的类型是Double的包装类,可以返回null
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool myTool = new Tool(2.9, 0);
if(myTool.div() != null) {
System.out.println("结果是" + myTool.div());
}
}
}
class Tool{
double num1;
double num2;
public Tool(double num1, double num2) {
this.num1 = num1;
this.num2 = num2;
}
public Double div() {
if(num2 == 0){
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
return null;
} else {
return this.num1 / this.num2;
}
}
}7.在类中传入其他类的实例,并调用其方法
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PassObject myFunction = new PassObject();
Tool myTool = new Tool(2.0);
myFunction.printAreas(myTool, 3);
}
}
class Tool{
double r;
public Tool(double r) {
this.r = r;
}
public double area() {
return Math.PI * r * r;
}
public void setC(double n) {
this.r = n;
}
}
class PassObject {
public void printAreas(Tool myCircle, int times) {
for(int i = 1; i <= times; i++)
{
myCircle.setC(i);
System.out.println(myCircle.area());
}
}
}8.综合实验题目:猜数字
(还可以在类的封装上加以改进将People类和输入类封装在一个游戏类中通过在主函数中创建的游戏类来启动游戏,在这里不多过多介绍)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
People myPeople = new People();
Scanner myScanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
System.out.println("请输入数字");
myPeople.setTarget(myScanner.nextInt());
if(myPeople.complete()) {
System.out.println("游戏结束");
break;
}
}
}
}
class People {
int target;
Machine myMachine = new Machine();
int flag = myMachine.create();
public void setTarget(int target) {
this.target = target;
}
public boolean complete() {
if(flag == target) {
System.out.println("结果正确");
return true;
} else if(flag < target) {
System.out.println("结果大了,请继续");
return false;
} else {
System.out.println("结果小了,请继续");
return false;
}
}
}
class Machine {
int target;
public int create(){
return (int)(Math.random() * 100) + 1;
}
}java面向对象的基础部分到此为止,接下来会进入IDEA的使用,包,访问修饰符,封装的部分

