Java笔记
反射
reflection
引出反射
我们需要怎样才可以读出配置文件的内容,并调用配置文件的方法
配置文件
classPath = com.reflection.Cat
method = hi目标类文件
package com.reflection;
public class Cat {
public void hi() {
System.out.println("hi");
}
}问题实现
第一点很容易,我们通过创建properties在进行加载,就可以很容易的得到配置中的内容
public class ReflectionQuestion {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "src\\re.properties";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(filePath));
String classPath = properties.getProperty("classPath");
String method = properties.getProperty("method");
System.out.println(classPath + " " + method);
}
}但是我们要怎样取创建配置文件中的对象,和调用对应的方法呢?
我们暂时还没有在不通过在不修改源码的情况下控制程序的办法,在这里我们就需要使用到反射机制来解决,以下是一个快速入门
快速入门
我们需要以下的几个步骤
1.加载类,返回Class类型的对象
//加载类运用一个Class的对象接收类的路径
Class cls = Class.forName(classPath);2.通过类得到你加载的类Cat对象实例
//通过Class对象的实例调用newInstance获取到对应类路径下对象的实例
//(编译类型是一个Object)(运行类型是对应的类型)
Object obj = cls.newInstance();3.通过类对象调用getMethod方法得到对应参数名称的方法,存在Method对象中(将方法视为一个对象)
//通过cls类调用方法getMethod获取方法
Method method01 = cls.getMethod(method);4.最后通过方法对象调用invoke传入对象,完成调用
//最后通过方法对象调用invoke传入对象,完成调用
method01.invoke(obj);完整代码
可以实现不修改源码的基础上修改程序的内部逻辑
public class ReflectionQuestion {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String filePath = "src\\re.properties";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(filePath));
String classPath = properties.getProperty("classPath");
String method = properties.getProperty("method");
Class cls = Class.forName(classPath);
Object targetClass = cls.newInstance();
Method targetMethod = cls.getMethod(method);
targetMethod.invoke(targetClass);
}
}输出结果
class com.reflection.Cat
hi修改测试
通过修改配置文件,创建一个狗类,调用其中的say方法
配置文件
classPath = com.reflection.Dog
method = say狗类
package com.reflection;
public class Dog {
public void say () {
System.out.println("大狗大狗叫叫叫~~");
}
}运行结果
大狗大狗叫叫叫~~反射机制原理
原理
1.反射机制允许程序在程序执行期间借助Reflection API获取任何类的内部信息(包括成员变量,构造器,成员方法),并能够操作对象的属性以及方法(反射在设计模式和底层框架都会用的到
2.加载完类后,堆中产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个类只有一个Class对象),这个对象包含了类的完整结构信息,通过这个对象得到类的结构。而这个对象就像是一面镜子,透过这个镜子可以看到类的结构(所以称之为反射)
反射机制原理图
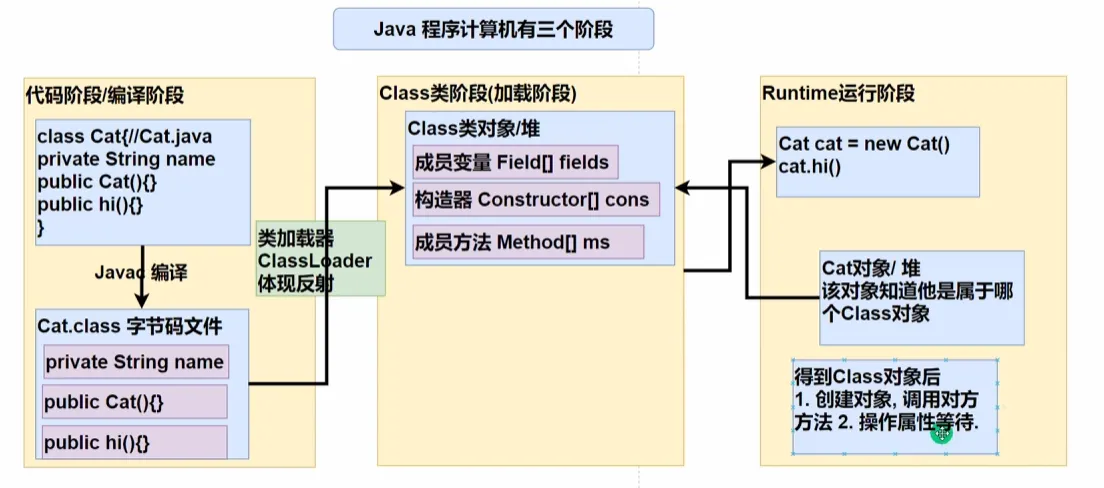
反射(Reflection)的核心来源是 Java 的 Class 对象,这个对象是程序在 Class 类阶段(加载阶段) 通过 ClassLoader 类加载器,加载后创建的。
在底层编译时
类加载器(ClassLoader)会将字节码文件加载到 JVM 中,并转换为 Class 类对象,其中包含:
- 字段信息(Field[] fields)
- 构造器信息(Constructor[] cons)
- 方法信息(Method[] ms)
这些信息是 Java 反射的基础,通过 Class 对象,Java 代码可以动态地获取类的详细结构,并在运行时操作类的成员(方法、变量等)。
对用户而言
Java 允许开发者使用反射机制操作 Class 对象
反射的方式:
- 通过
Class对象获取类的信息(字段、方法、构造器)。 - 通过
Field访问类的字段。 - 通过
Method调用类的方法。 - 通过
Constructor创建对象实例。
反射的优缺点
1.优点:可以动态的创建和使用对象(也是框架的底层核心),使用灵活,没有反射机制,框架就会失去底层支持
2.使用反射基本是解释执行,对执行速度有影响(和传统方式时间差距很大)
有一个setAccessible方法可以操作访问安全检查的开关以此来提升反射的效率
反射相关的类
Class
代表一个类,Class对象表示在某个类加载后在堆中的对象
Class cls = Class.forName(classPath);
//创建Class对象
Object obj = cls.newInstance();
//通过Class对象获取对应实例1.Class也是类,继承于Object类
2.Class类对象不是new实例化出来的,而是系统创建的
3.对于某个类的Class类对象,在内存中只有一份,因为类只加载一次
4.每个类的实例都会记得自己是由哪一个Class实例所生成的
5.通过Class对象可以完整的得到一个类的完整结构(API调用)
6.Class对象是存放在堆中的
7.类的字节码二进制数据,是放在方法区的,称之为类的元数据(包括方法代码,变量名,方法名,访问权限等)
Method
代表类的方法,Method对象表示某个类的方法
Method method01 = cls.getMethod(method);
//获取方法对象
method01.invoke(obj);
//通过invoke传入类对象实例调用方法Field
代表类的成员变量,Field对象表示某个类的成员变量
Field nameField = cls.getField("name");
//获取成员变量对象
System.out.println(nameField.get(obj));Constructor
代表类的构造方法,Constructor对象表示某个类的构造器
Constructor constructor1 = cls.getConstructor();
//不带参数的构造器
System.out.println(constructor1);
Constructor constructor2 = cls.getConstructor(String.class);
//带参数的构造器需要传入String类的Class对象
System.out.println(constructor2);当然也可以调用构造器对象构造类的对象实例
Class常用方法(入门)
forName
获取类的对象
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Cat");Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Cat");
System.out.println(cls);//class com.reflection.Cat
System.out.println(cls.getClass());//class java.lang.Class前一个输出是哪一个类的Class对象,后一个输出类对象
getPackage
获取类的包名
System.out.println(cls.getPackage());
//package com.reflectiongetName
获取类的全路径
System.out.println(cls.getName());
//com.reflection.CatnewInstance
通过类实例创建对应类的实例
Object obj = cls.newInstance();
Cat cat = (Cat)obj;
cat.hi();getField
获取类的属性(无法获取私有属性)
Field field = cls.getField("name");
System.out.println(field.get(obj));获取所有属性
Field[] fields = cls.getFields();
for(Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field.get(obj));
}set
设置类属性的值
Object obj = cls.newInstance();
Field field = cls.getField("name");
field.set(obj, "来福");
System.out.println(field.get(obj));获取Class对象方式
在编程的时候一共可以有六种方式可供程序员使用获取Class对象
代码阶段
forName
使用前提:已知一个类的全类名,且类在类的路径下,可以通过Class的静态方法forName获取(可能会抛出ClassNotFound异常)
应用场景:多用于配置文件,获取类全路径,加载类
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Cat");加载阶段
类.class
从类加载器中获取
使用前提:已知具体的类,通过类的class方法获取,该方式是最为可靠的,程序性能最高
应用场景:多用于参数传递,比如通过反射得到对应构造器对象
Class cls = Cat.class;运行阶段
对象.getClass
使用前提:某一个类的实例已经存在,通过该实例的getClass方法获取Class对象
应用场景:通过创建好的对象获取Class对象
Cat cat = new Cat();
Class cls = cat.getClass();通过类加载器
调用类加载器的loadClass方法获取
ClassLoader classLoader = cat.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class<?> cls = classLoader.loadClass();基本数据类型类对象
数据类型.class
Class<Integer> cls = int.class;
System.out.println(cls);//int 这里隐含了自动拆装箱包装型类对象
调用包装类的静态属性TYPE获取
Class<?> cls = Integer.TYPE;类加载
反射机制是Java实现动态语言的关键,也就是通过反射实现动态加载
动态加载与静态加载
静态加载
编译时加载相关的类,如果没有则报错,依赖性较高
动态加载
运行时加载需要的类,如果没有用到缺失的类,就不会报错,降低了依赖性
代码示例
以下是一个动态加载的代码示例:
例如我有一个Cat类,一个House类,但是实际上只有Cat类是在代码中声明,我们利用静态加载一个Cat 和一个House类,代码不通过编译
Cat cat = new Cat();
House house = new House();//编译报错,没有House类但是我们可以通过类加载实现动态加载,只有在运行的时候没有获取到对应的类时候才会发出运行时错误
public class Class01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
char key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case 1:
Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Cat");
Object obj1 = cls.newInstance();
break;
case 2:
Class cls2 = Class.forName("com.reflection.House");
Object obj2 = cls2.newInstance();
break;
}
}
}在输入2的时候报错
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.reflection.House类加载的流程图
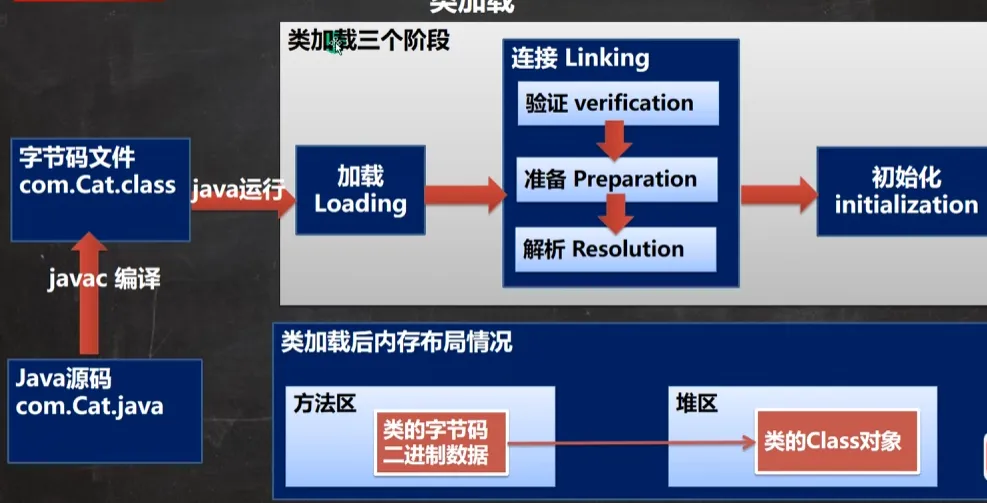
加载阶段(由JVM控制)
JVM机将字节码从不同的数据源(class文件、jar包,网络)转化为二进制字节流加载到内存中,并且生成代表该类的java.lang.Class对象
连接阶段(由JVM控制)
验证
确保Class字节流中的信息符合当前虚拟机的要求,并且不会危害虚拟机的安全(这个阶段是可以手动关闭的)
在编译运行的时候:使用-Xverify
准备
JVM在该阶段对静态变量,分配内存,并默认初始化(0,null,false等),这些变量所使用的内存都在方法区中进行分配
以一个类来举例
class A {
public int n1 = 10;
//n1是实例属性,不是静态变量,在准备阶段是不会分配内存的
public static int n2 = 20;
//n2是静态变量,分配内存,初始化为0,在后续才会进行赋值
public static final int n3 = 30;
//n3是一个常量,分配内存,初始直接进行赋值30
}解析阶段
虚拟机将常量池中的符号引用替换为直接引用的过程
初始化(由程序员控制)
1.到初始化阶段才开始执行类中定义的Java程序代码,此阶段执行的是
2.
3.虚拟机会保证一个类的
正是通过3的线程加锁,才保证了某一个类的对象在堆中只存在一个
在代码编写的时候:有一个setAccessible(爆破)方法可以操作访问安全检查的开关以此来提升反射的效率
获取类信息
相关方法
现有一个类Person
@Deprecated
public class Person extends AA implements IL{
public int pub = 0;
int def = 0;
private int pri = 0;
public Person() {}
public Person(int pub, int def, int pri) {
this.pub = pub;
this.def = def;
this.pri = pri;
}
public void say(){}
void hi(){}
}Class类
getName
获取全类名
Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
System.out.println(cls.getName());
//com.reflection.PersongetSimpleName
获取简单类名
Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
System.out.println(cls.getSimpleName());//PersongetFields
获取所有public修饰的属性,包含本类以及父类
Field[] fields = cls.getFields();
for(Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}public int com.reflection.Person.pubgetDeclaredFields
获取本类中所有属性
Field[] fields = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}public int com.reflection.Person.pub
int com.reflection.Person.def
private int com.reflection.Person.prigetMethods
获取本类中由public修饰的所有方法,包含本类以及父类
Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Method[] methods = cls.getMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method.getName());
}say
wait
wait
wait
equals
toString
hashCode
getClass
notify
notifyAllgetDeclaredMethods
获取本类中所有方法
Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Method[] methods = cls.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}void com.reflection.Person.hi()
public void com.reflection.Person.say()getConstructors
获取public修饰的构造器,包含本类
Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Constructor[] connstructors = cls.getConstructors();
for(Constructor connstructor : connstructors) {
System.out.println(connstructor);
}public com.reflection.Person()
public com.reflection.Person(int,int,int)getDeclaredConstructors
获取本类所有的构造器
public com.reflection.Person()
public com.reflection.Person(int,int,int)getPackage
以Package的形式返回包信息
Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
System.out.println(cls.getPackage());
//package com.reflectiongetSuperclass
以Class的形式返回父类的信息
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
System.out.println(cls.getSuperclass());
//class com.reflection.AA
}getInterfaces
以Class的形式返回接口信息
public class Class01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Class[] interfaces = cls.getInterfaces();
for(Class anInterface : interfaces)
System.out.println(anInterface);
//interface com.reflection.IL
}
}getAnnotations
以Annotation数组的形式返回注解信息
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Annotation[] annotations = cls.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation annotation : annotations)
System.out.println(annotation);
//@java.lang.Deprecated()
}Filed类
getModifiers
以int形式返回修饰符
默认修饰符0 ,public 1 , private 2 , protected 4 ,static 8 ,final 16 public+static 9(1 + 8)
Field field = cls.getField("pub");
//注意通过getField只能获取public修饰的属性
System.out.println(field.getModifiers());//1 (public)getType
以Class形式返回类型
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Field field = cls.getField("pub");
System.out.println(field.getType());//intgetName
返回属性名
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Field field = cls.getField("pub");
System.out.println(field.getName());//pubMethod类
getModifiers
以int形式返回修饰符
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Method method = cls.getMethod("say");
System.out.println(method.getModifiers());//1getReturnType
以Class形式返回类型
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Method method = cls.getMethod("say");
System.out.println(method.getReturnType());//voidgetName
返回方法名
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Method method = cls.getMethod("say");
System.out.println(method.getName());//saygetParameterTypes
以Class数组返回参数类型数组
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Method method = cls.getMethod("say");
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();Constructor类
和Method类基本一致,没有getReturnType方法(没有返回值)
反射爆破
反射爆破创建实例
有以下几个构造器
public Person() {}
public Person(int pub) {
this.pub = pub;
}
public Person(int pub, int def, int pri) {
this.pub = pub;
this.def = def;
this.pri = pri;
}
private Person(int pub, int def) {
this.pub = pub;
this.def = def;
}大体分为两种方式
方式一:调用类中pulic修饰的无参构造器
方式二:调用类中的指定构造器
Constructor类相关方法
setAccessible
是Java程序设计者留的后门,可以破解私有构造器的限制
爆破(暴力破解)
constructor.setAccessible(true);newInstance
调用构造器
Object obj = constructor.newInstance(10);//通过构造器创建对象Class类相关方法
newInstance
调用类中的无参构造器,获取对应类的对象
Object obj = cls.newInstance();getConstructor
根据参数列表,获取对应的构造器对象(获取public构造器对象)
Constructor<?> constructor = cls.getConstructor(int.class);//获取到公有的构造器getDecalaredConstructor
根据参数列表,获取对应的构造器对象(获取本类所有的构造器对象)
用普通的方式无法通过private修饰的构造器创建对象实例,但是通过反射可以实现
但是后续调用私有构造器需要爆破(暴力破解private)(单独使用newInstance会发生运行错误)
Constructor<?> constructor = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class,int.class);//获取到所有的构造器通过爆破使用私有构造器
Constructor<?> constructor = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class,int.class);//获取到所有的构造器
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = constructor.newInstance(10, 29);//通过构造器创建对象
System.out.println(obj);//pub 10 def 29 pri 0反射爆破操作属性
访问属性的相关方法
获取Field对象
Field f = class对象.getDeclaredField(属性名称)
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("pri");爆破
field.setAccessible(true);访问
设置属性值
f.set(obj, 值)
field.set(obj, 100);获取属性值
f.get(obj)
field.get(obj)如果是静态属性,则set和get中的obj参数可以写为null
private修饰的属性值
public class Class01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Constructor<?> constructor = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, int.class, int.class);
//获取到所有的构造器
Object obj = constructor.newInstance(10, 29, 101);//通过构造器创建对象
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("pri");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, 100);
System.out.println(field.get(obj));//100
}
}反射爆破操作方法
访问方法相关方法
getDeclaredMethod
获取类所有的方法
Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("hi");setAccessible
设置方法爆破
method.setAccessible(true);invoke
传入class类对象实例调用方法
如果是静态方法传入null即可
invoke方法参数后是一个可变参数,可供传入参数
Object returnValue = method.invoke(obj);//静态方法hi在反射中如果有返回值统一返回Object类型的值
通过反射调用private方法
public class Class01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.Person");
Constructor<?> constructor = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, int.class, int.class);//获取到所有的构造器
Object obj = constructor.newInstance(10, 29, 101);//通过构造器创建对象
Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("hi");
method.setAccessible(true);
method.invoke(obj);//静态方法hi
}
}课后习题
例题一
1.定义PrivateTest类,由私有属性name,属性值为hellokitty
2.提供getName公共方法
3.创建PrivateTest类,利用Class类得到私有属性name属性,修改name属性值
4.使用getName方法打印name属性值
题解
写出PrivateTest类
package com.reflection;
public class PrivateTest {
private String name = "hellokitty";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}主方法调用
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("com.reflection.PrivateTest");
Object obj = cls.newInstance();
Field name = cls.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(obj, "New name");
Method getName = cls.getMethod("getName");
Object invoke = getName.invoke(obj);
String target = (String) invoke;
System.out.println(target);//New name
}
}例题二
1.利用Class类的forName方法得到File类的class对象
2.在控制台打印出File类的所有构造器
3.通过newInstance的方法创建File对象,并创建 E:\mynew.txt 文件
public class FileTest{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("java.io.File");
Constructor<?>[] constructors = cls.getDeclaredConstructors();
for(Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
Constructor<?> constructor = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
Object obj = constructor.newInstance("e:\\JavaFile\\mynew.txt");
Method method = cls.getMethod("createNewFile");
method.invoke(obj);
}
}
