JavaWeb笔记
之前Maven没有配置好导致了JavaWeb的环境配置比较困难,去大概了解了一下Maven构建的相关知识,现在可以快速通过坐标导入相关的jar包了,马上开始Servlet的学习
Servlet
入门使用
我使用的是Maven构建的Servlet程序,不需要web.xml进行注册,只需要使用@WebServlet注解完成绑定即可访问使用
新建一个类,实现Servlet的接口方法
1
2
| @WebServlet("/hello")
public class HelloServlet implements Servlet
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| @Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Hello Servlet");
}
@Override
public String getServletInfo() {
return "";
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
|
注意:在Maven构建的Servlet程序中,index.jsp要放在src/main/webapp目录下,才可以被默认访问到
配置完毕的时候,我们运用浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080/ServletTest/hello 即可调用实现servlet接口的实现类中的相关方法
运行流程
以下是一个调用的流程图:
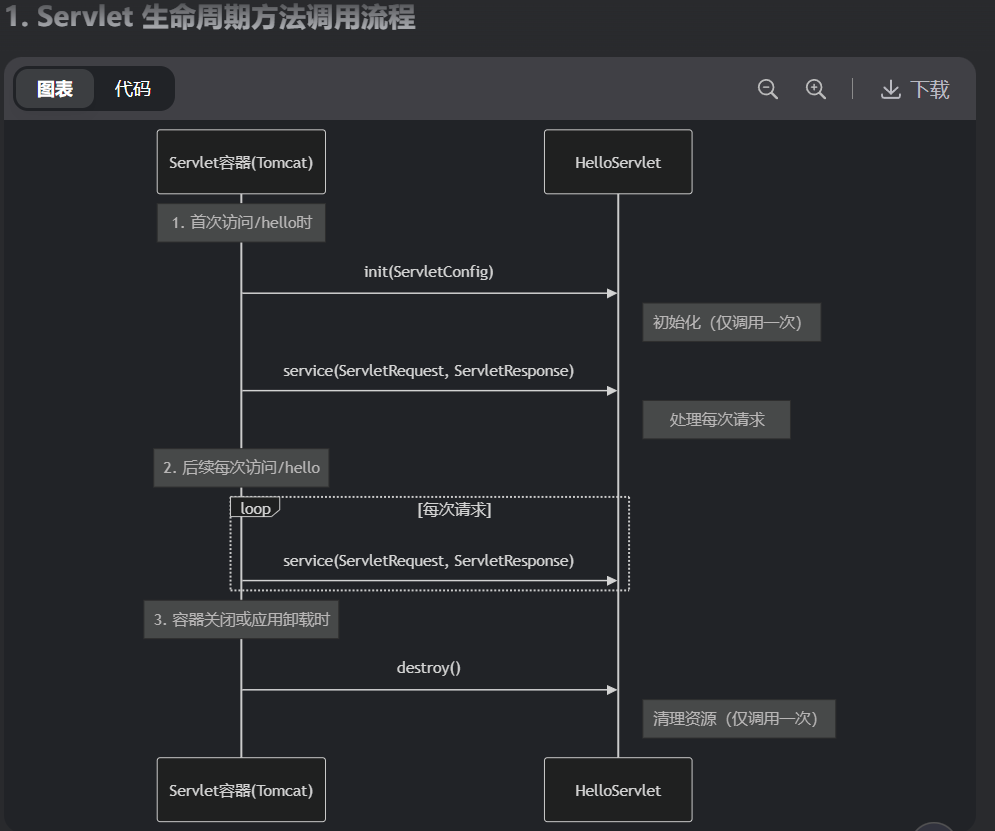
1.执行Servlet构造方法
2.执行init初始化方法
3.执行
4.执行destroy销毁方法
前两个方法在初次时调用,第二次访问/hello时,只调用service方法
1
2
3
4
| create Servlet
init Servlet
Servlet Running
Servlet Running
|
sevice方法
用一个html页面运用submit提交,跳转到对应的路径下也会被Servlet捕获并且调用相关方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/ServletTest/hello" method="post">
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Servlet Running");
HttpServletRequest Request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
String method = Request.getMethod();
System.out.println(method);
}
|
通过ServletRequest servletRequest的子类型的getMethod方法可以得到请求的类型(Post/Get)
一般而言,我们在处理两种不同的请求类型的时候进行方法化处理,分别调用不同的处理操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Servlet Running");
HttpServletRequest Request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
String method = Request.getMethod();
switch (method) {
case "GET":
System.out.println("GET Method");
doGet();
break;
case "POST":
System.out.println("POST Method");
doPost();
break;
}
}
|
HttpServlet实现
在实际的开发中,很少通过实现servlet接口实现servlet程序,而是继承其子类HttpServlet来实现
1.编写一个类去集成HttpServlet类
2.根据业务需要重写doGet或者doPost方法
3.到web.xml配置Servlet程序的访问地址(我通过@WebServlet(“/test”)完成)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @WebServlet("/test")
public class ServletTest extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Servlet Get Called");
super.doGet(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Servlet Post Called");
super.doPost(req, resp);
}
}
|
继承关系
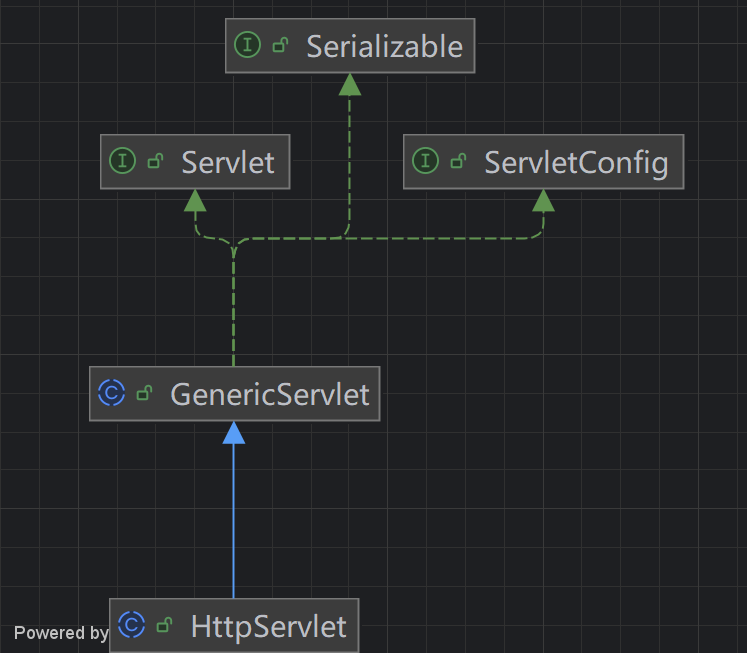
GenericServlet实现了Servlet接口,并做了一些空实现,持有一个ServletConfig类的引用,并对ServletConfig的使用做一些方法
HttpServlet抽取类实现了service方法,并实现了请求的分发处理
1
| String method = req.getMethod();
|
而其中调用的doGet和doPost默认抛出异常,不支持请求,我们在实际使用的时候根据需要重写方法实现业务逻辑即可
ServletConfig类
注解Servlet
首先运用注解设置访问地址以及初始化参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @WebServlet(
urlPatterns = "/hello", // 访问路径
initParams = {
@WebInitParam(name = "name", value = "John"),
@WebInitParam(name = "age", value = "25")
}
)
|
从类名来看,是Servlet程序的配置信息类
Servlet程序和ServletConfig对象都是由Tomcat负责创建,我们负责使用
Servlet程序默认是第一次访问的时候创建,ServletConfig是每个Servlet程序创建的时候,就创建一个ServletConfig对象(其中封装了一些信息)
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public interface ServletConfig {
String getServletName();
ServletContext getServletContext();
String getInitParameter(String var1);
Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames();
}
|
三大作用
1.可以获取Servlet程序的别名servlet-name的值
2.获取初始化参数init-param
3.获取ServletContext对象
传递初始化参数的init方法,以及ServletConfig的使用方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println(servletConfig.getServletName());
System.out.println(servletConfig.getInitParameter("name"));
System.out.println(servletConfig.getServletContext());
System.out.println("init Servlet");
}
|
注意要点
HttpServlet在重写init方法的时候需要调用super.init去获取到父类的config类,否则会发生空指针异常
1
2
3
4
5
| @Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
super.init(config);
System.out.println(config.getServletName());
}
|
因为HttpServlet的config没有被赋予GenericServlet的config信息,指向为空
1
2
3
4
| public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
|
ServletContext类
定义
是一个接口,表示Servlet上下文对象
一个Web工程,只有一个ServletContext对象实例
ServletContext是一个域对象(可以像Map一样存取数据的对象,域指的是存取数据的操作范围)
| 比较 |
存数 |
取数 |
删除数据 |
| Map |
put |
get |
remove |
| 域对象 |
setAttribute |
getAttribute |
removeAttribute |
ServletContext是在Web工程部署启动的时候创建的,在Web工程停止的时候销毁
作用
1.获取web.xml中配置的上下文参数context-param
2.获取当前的工作路径,格式:/工程路径
3.获取工程部署后在服务器硬盘上的绝对路径
4.像Map一样存取数据
实际使用
由于我的Servlet程序没有设置web.xml,全局上下文变量是通过一个WebListener完成的,其中存储了一个global和一个version
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package com.listener;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
@WebListener
public class ContextListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
sce.getServletContext().setAttribute("global", "Hello World");
sce.getServletContext().setAttribute("version", "1.0.0");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("contextDestroyed");
}
}
|
而要在Servlet程序中调用,则通过getServletContext获取到上下文,再通过getAttribute类似map一样的操作取出对应的值
以下是HttpServlet的实现类,其中有一个getServletContext的封装方法以调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @WebServlet("/new")
public class NewServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String global = (String)getServletContext().getAttribute("global");
String version = (String)getServletContext().getAttribute("version");
System.out.println("Servlet Get Called" + global + " " + version);
}
}
|
我们还可以通过Context获取工作路径与部署绝对路径
注意事项:getRealPath方法在一些 非文件系统部署(比如 WAR 包部署到云服务器)中可能返回 null,因此用需要额外小心
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String contextPath = getServletContext().getContextPath();
String realPath = getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
System.out.println(contextPath);
System.out.println(realPath);
}
|
HTTP协议
指客户端和服务端通信时发送数据需要遵守的规则,HTTP协议中的数据称为报文,其中的请求分为GET请求和POST请求
GET请求
1.请求行:请求的方式,请求的资源路径,请求的协议和版本号
2.请求头: key:value 组成,不同的键值对表示不同的含义

Post请求
1.请求行:请求的方式,请求的资源路径,请求的协议和版本号
2.请求头: key:value 组成,不同的键值对表示不同的含义
空行:请求头和请求体之间有空行
3.请求体:===>>>就是发送给服务器的数据
这里表单中有隐藏数据login username,将这两个信息发送给服务器
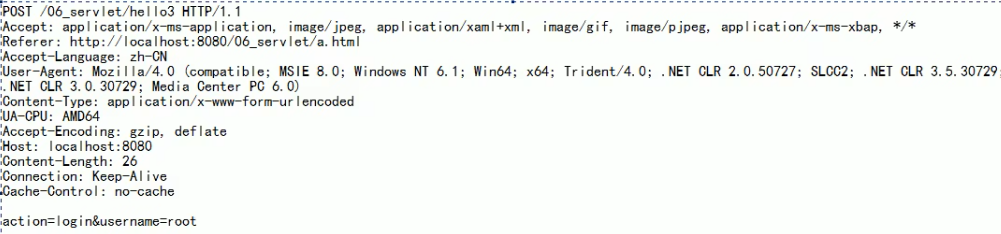
常见的请求头
Accept:告诉服务器,客户端可以接收的数据类型
Accept-Language:告诉服务器客户端可以接收的语言类型,zh_CN、zh_ENG
User-Agent:浏览器的信息
Accept-Encoding:告诉服务器,客户端可以接收的数据编码(压缩)格式
Host:表示请求的服务器ip和端口号
Connection:告诉服务器当前连接如何处理,常见的有两种,Keep-Alive和Closed
Referer:表示请求发起时,浏览器地址栏中的地址从哪里来
Content-Type:表示发送的数据类型(图中的表示多段数据提交,以流形式提交)
Content-Length:发送的数据长度
Cache-Control:表示如何控制缓存,no-cache表示不缓存
Get请求和Post请求区分
Get:
form method=get a标签 link标签引入css script引入js文件 img标签引入图片 iframe引入html页面 在浏览器地址栏中输入访问地址回车
Post:
form method=post
响应HTTP协议格式
格式
1.响应行:响应的协议与版本号 响应状态码 响应状态描述符
2.响应头: key:value 不同的响应头,有不同的含义
空行
3.响应体:—>>>回传给客户端的数据
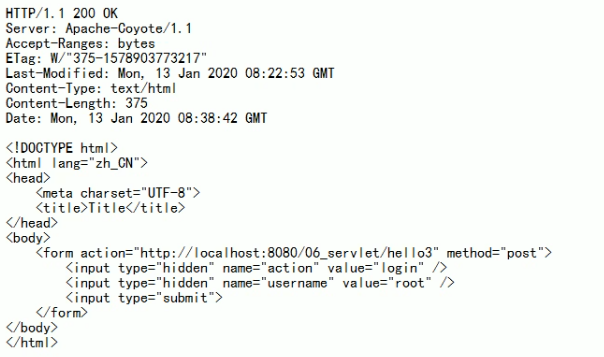
常见响应码
200:表示请求成功
302:表示请求重定向
404:表示请求被服务器收到,但是预期数据不存在(请求地址出错)
500:表示服务器已经收到请求,但是服务器内部错误(代码错误,发生不可预期的错误)
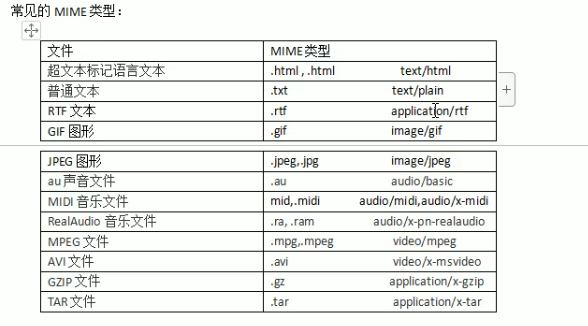
MIME
MIME是HTTP协议中的数据类型,全称为多功能internet邮件扩充服务,MIME类型的格式是“大类型/小类型”,并与某一种文件的扩展名相对应