Java笔记
Map接口
定义及性质
双列集合
存放的是K-V
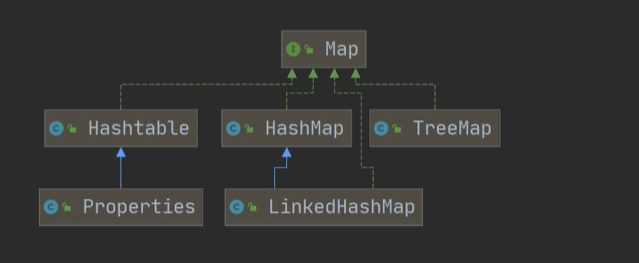
Map接口下有三个重要的类Hashtable ,HashMap , TreeMap,其中HashMap时使用频率最高的
1.Map与Collection并列存在,保存具有映射关系的数据,Key-Value
2.Map中的key和value可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装在HashMap$Node对象中
3.Map中的key不允许重复,原因和HashSet一样
4.Map中的key可以重复
5.Map中的key和value可以为null,但是key中的null只能有一个,而value不做限制
6.常用类String类可以作为Map的key
7.key和value之间存在单向的一对一关系,即通过指定的key总可以找到对应的value
8.map存放数据k-v,一对key-value是存放在HashMapNode中的
为了程序员遍历方便,还会创建EntrySet集合,该集合放入的是Entry(事实上是将EntrySet中的table 存储的Entry节点指向Map的Node)
1
| transient Node<K,V>[] table;
|
1
| transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
|
Map常用方法
put
放入Map集合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "jack");
map.put(10, "hello");
System.out.println(map);
}
}
|
可见put当key重复的时候其实起的是替换的作用
而value是可以重复的,只要key不一样即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "hello");
map.put(13, "hello");
System.out.println(map.size());
}
}
|
get
通过key返回value
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "hello");
map.put(13, "hello");
System.out.println(map.get(12));
}
}
|
remove
根据key删除映射关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "hello");
map.remove(16);
System.out.println(map);
}
}
|
size
获取元素个数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "hello");
System.out.println(map.size());
}
}
|
isEmpty
判断元素个数是否为0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "hello");
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
}
}
|
clear
清除所有元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "hello");
map.clear();
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
}
}
|
containsKey
查找键是否存在
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "hello");
System.out.println(map.containsKey(10));
}
}
|
Map接口的遍历方式
总共有六种方式
1
2
3
| Set<K> keySet();
Collection<V> values();
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
|
keySet
1、2、通过取出Key的Set集合,遍历Set集合中的Key,还可以通过Key取出Map中的Value
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "hello");
Set keySet = map.keySet();
for (Object key : keySet) {
System.out.println(key + ": " + map.get(key));
}
Iterator iterator = keySet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object key = iterator.next();
System.out.println(key + ": " + map.get(key));
}
}
}
|
values
3、4、取出Values,进行遍历(用接口Collection接收)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "hello");
Collection values = map.values();
for(Object obj : values) {
System.out.print(obj + " ");
}
Iterator iterator = values.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.print(obj + " ");
}
}
}
|
entrySet
5、6、通过取出Entry的Set集合,将entry(Object)转为Map.Entry,再通过Map.Entry实现的getKey和getValue方法取出Map中的KV
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, "lory");
map.put(16, "marry");
map.put(10, "hello");
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
for(Object o : entrySet) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) o;
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue());
}
Iterator iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Object o = iterator.next();
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) o;
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
|
综合案例
输出集合中工资大于18000的键值以及对应老师toString方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| public class Map_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(12, new Teacher("lory", 22, 12000 ));
map.put(16, new Teacher("marry", 44, 13000));
map.put(13, new Teacher("jack", 55, 19000));
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Object obj : entrySet) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) obj;
Teacher teacher = (Teacher) entry.getValue();
if(teacher.salary > 18000) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
}
class Teacher {
String name;
int age;
double salary;
public Teacher(String name, int age, double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "教师 " + name + " " +
"今年 " + age + " 岁";
}
}
|
Map的实现子类
HashMap
1.Map接口的常用实现类是HashMap,Hashtable,Properties
2.其中HashMap是Map接口中使用频率最高的实现类
3.通过key-value的方式存储数据
4.和HashSet一样,不保证映射的顺序,因为底层是由hash表的方式来存储的
5.HashMap没有实现线程同步,因此线程不安全
HashMap扩容上而言和HashSet一模一样,扩容因子是0.75扩容为原来的两倍,默认初始化为16
Hashtable
1.放入的元素为键值对Key-Value
2.Hashtable的键和值都不能为null(否则会派出NullPointException)
3.Hashtable的使用和HashMap基本相同
4.Hashtable是线程安全的,而HashMap不是线程安全的
HashMap与Hashtable对比
HashMap线程不安全而Hashtable安全
HashMap效率优于Hashtable
Hashtable不允许null键值和null数据
Properties
1.Properties类继承于Hashtable并且实现了Map接口,是一种键值对的形式保存数据
2.使用方式和Hashtable类似
3.Properties还可以用于从xxx.properites文件中,加载数据带Properties类对象,并进行读取和修改(广泛用于从配置文件中读取账号和密码,避免硬编码)
4.xxx.properites文件通常作为配置文件,在后续的IO流会介绍
代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class Properties_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put(18, "lory");
properties.put(19, "marry");
properties.put(20, "jack");
System.out.println(properties.get(18));
}
}
|
LinkedHashMap
和LinkedHashSet与HashSet的关系类似
是HashMap的有序排列(通过双向链表维护)
TreeMap
直接实现Map接口
保证插入时的键有序(通过传入一个Comparator接口比较器)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class TreeMap01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
int i1 = (Integer)o1;
int i2 = (Integer)o2;
return i1 - i2;
}
});
treeMap.put(1, "Tom");
treeMap.put(3, "Marry");
treeMap.put(4, "Lory");
treeMap.put(2, "Thrinisty");
System.out.println(treeMap);
}
}
|
Collections工具类
定义
1.Collections是一个操作Set,List,Map集合的工具类
2.提供了一系列的静态方法对集合元素进行排序,查询,修改等操作
常用的工具类
reverse(List)
将List中的元素顺序反转
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class List01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("A");
list.add(10);
list.add(true);
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
shuffle(List)
将List中的元素随机排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class List01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("A");
list.add(10);
list.add(true);
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
sort(List,Comparator)
将List中的元素按照指定功能排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class List01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("A");
list.add("BFXC");
list.add("DVB");
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() {
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
String s1 = (String)o1;
String s2 = (String)o2;
return s1.compareTo(s2);
}
});
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
swap(List,int, int)
交换List中的两个对应下标中的元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class List01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("A");
list.add("BFXC");
list.add("DVB");
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
Collections.swap(list, 3, 2);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
max(Collection,Comparator)
按照指定顺序返回最大元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public class List01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("A");
list.add("BFXC");
list.add("DVB");
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
System.out.println(Collections.max(list, new Comparator() {
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
String s1 = (String) o1;
String s2 = (String) o2;
return s1.length() - s2.length();
}
}));
}
}
|
frequency(Collection, Object)
返回指定集合中指定元素出现的次数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class List01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("A");
list.add("BFXC");
list.add("DVB");
list.add("A");
list.add("A");
System.out.println(Collections.frequency(list, "A"));
}
}
|
copy(List dest,List src)
将src的内容复制到dest中
要求新的集合大小大于旧的,否则或抛出异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class List01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("A");
list.add("BFXC");
list.add("DVB");
List list1 = new ArrayList();
list1.add(" ");
list1.add(" ");
list1.add(" ");
Collections.copy(list1, list);
System.out.println(list1);
}
}
|
如下这种方式也不行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class List01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("A");
list.add("BFXC");
list.add("DVB");
List list1 = new ArrayList(4);
list1.add(" ");
Collections.copy(list1, list);
System.out.println(list1);
}
}
|
new ArrayList(4) 只是设置初始容量(capacity),但 size() 仍然是 0。
调用 list1.add(" ") 后,list1.size() 变为 1,但 list.size() 是 3。
目标列表 list1 的长度(1) < 源列表 list 的长度(3),不满足 copy() 的条件。
replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal)
使用新值替换所有旧值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class List01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("A");
list.add("BFXC");
list.add("A");
list.add("A");
Collections.replaceAll(list, "A", "B");
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
简答题