听课笔记
Java中的递归
递归在算法中属于比较复杂的一类了,在这里也希望在 java 的学习中复习算法
一个简单的入门案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class Object{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool Mytool = new Tool();
Mytool.test(4);
}
}
class Tool{
public void test(int n) {
if(n > 2) {
test(n - 1);
}
System.out.println(n);
}
}
|
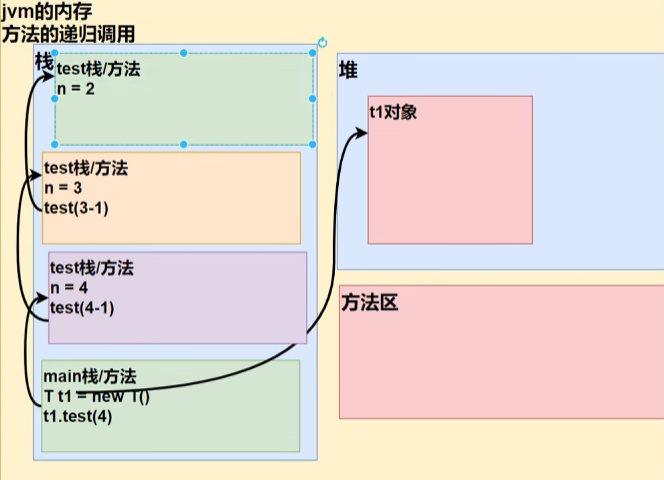
运行结果
要等递归的方法结束后才执行递归调用主体函数中的输出,所以结果是从2到4
计算阶乘
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Object{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool Mytool = new Tool();
System.out.println(Mytool.Printni(3));
}
}
class Tool{
public int Printni(int n) {
if(n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return Printni(n - 1) * n;
}
}
}
|
递归的要点
1.执行方法的时候会生成一个新的独立的栈空间
2.方法的局部变量是独立的不会相互影响
3.如果方法中使用的是引用类型的数据变量,就会共享该引用类型的数据
4.递归必须得指定退出的条件,在执行时也必须向退出的条件逼近
5.当一个方法执行完毕的时候,或 return 就会返回到调用函数中
递归的经典例题
斐波那契数列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import java.util.Scanner;
public class Object{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner myScanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入斐波那契数列的第几个数");
int target = myScanner.nextInt();
Tool myTool = new Tool();
System.out.println("斐波那契的第"+ target + "个数是" + myTool.test(target));
}
}
class Tool{
public int test(int n) {
if(n == 1 || n == 2) {
return 1;
} else {
return test(n - 1) + test(n - 2);
}
}
}
|
猴子吃桃问题
猴子每天吃一般的桃子 再额外吃一个,第十天的时候有1个桃子可以吃,问第一天的时候有几个桃子
递推式:第n天的桃子 = (第 n - 1 个桃子 / 2)- 1
反递推式:第n天的桃子 =(第n + 1天的桃子 + 1) * 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import java.util.Scanner;
public class Object{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int target = 10;
Tool myTool = new Tool();
System.out.println(myTool.peace(1));
}
}
class Tool{
public int peace(int day) {
if(day == 10){
return 1;
} else {
return (peace(day + 1) + 1) * 2;
}
}
}
|
经典的回溯算法走迷宫题目
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| public class Object{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[][] = new int[8][7];
Tool myTool = new Tool();
for(int j = 0; j < arr[0].length; j++) {
arr[0][j] = 1;
arr[arr.length - 1][j] = 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i][0] = 1;
arr[i][arr[0].length - 1] = 1;
}
arr[3][1] = 1;
arr[3][2] = 1;
arr[2][2] = 1;
myTool.Print(arr);
System.out.println();
myTool.findWay(arr, 1, 1);
myTool.Print(arr);
}
}
class Tool{
public void Print(int arr[][]) {
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public boolean findWay(int map[][], int i, int j) {
if(map[6][5] == 2) {
return true;
} else {
if(map[i][j] == 0) {
map[i][j] = 2;
if(findWay(map, i + 1, j)) {
return true;
} else if(findWay(map, i, j + 1)) {
return true;
} else if(findWay(map, i - 1, j)) {
return true;
} else if(findWay(map, i, j - 1)) {
return true;
} else {
map[i][j] = 3;
return false;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
|
汉诺塔
简单的递归问题,一共分为三步,就和把大象塞进冰箱一样
1.打开冰箱(将A盘上的 n-1 个塔放在B盘)
2.放入大象(将A盘的最大盘放在C盘)
3.关闭冰箱(将B盘上的 n-1 个塔放在C盘)
在这里有一个值得注意的递归终止条件仅仅剩余一个盘,直接放入即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| import java.util.Scanner;
public class Object{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hanoi myHanoi = new Hanoi();
Scanner myScanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入汉诺塔的层数");
int count = myScanner.nextInt();
myHanoi.moveTower(count, 'A', 'B', 'C');
}
}
class Hanoi{
public void moveTower(int n, char a, char b, char c) {
if(n == 1) {
System.out.println("将" + a + "盘上的第一个塔移动到" + c);
} else {
moveTower(n - 1, a, c, b);
System.out.println("将" + a + "盘上的第一个塔移动到" + c);
moveTower(n - 1, b, a, c);
}
}
}
|
八皇后问题
将这一道例题分解为了三个部分来完成
1.设计了一个一维数组结构用于存放八个皇后,数组的下标代表了放置的行号,对应的数值部分是皇后放置的列数
2.八皇后递归的主体部分,要注意先将对应的皇后放入一维数组,在进行后续的递归调用
3.将递归的主体部分的结果返回至一个引用传回结果自增
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queen myQueen = new Queen();
int map[] = new int[8];
int result[] = {0};
myQueen.placeQueen(map, 0, result);
System.out.println(result[0]);
}
}
class Queen {
public void placeQueen(int arr[], int row, int rst[]) {
if(row == 8) {
rst[0]++;
return;
}
for(int col = 0; col < 8; col++) {
if(canPlace(arr, row, col)){
arr[row] = col;
placeQueen(arr, row + 1, rst);
}
}
}
public boolean canPlace(int arr[], int row, int col) {
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
if(arr[i] == col || arr[i] + i == col + row || arr[i] - i == col - row) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
|
递归的例题完成,接下来是Java中方法的重载,可变参数,构造器的笔记

